Estrogen receptor and aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathways
- PMID: 16862222
- PMCID: PMC1513070
- DOI: 10.1621/nrs.04016
Estrogen receptor and aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathways
Abstract
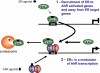
Estrogen receptors (ERs) and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) are ligand activated transcription factors and members of the nuclear receptor and bHLH-PAS superfamilies, respectively. AhR is involved in xenobiotic metabolism and in mediating the toxic effects of dioxin-like compounds. Crosstalk has been observed among AhR and nuclear receptors, but has been most well studied with respect to ER signaling. Activated AhR inhibits ER activity through a number of different mechanisms, whereas ERalpha has been reported to have a positive role in AhR signaling. Here we will discuss recent data revealing that dioxin bound AhR recruits ERalpha to AhR regulated genes. We will also consider the implications of ER recruitment to AhR target genes on ER and AhR signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Abdelrahim M., Ariazi E., Kim K., Khan S., Barhoumi R., Burghardt R., Liu S., Hill D., Finnell R., Wlodarczyk B., Jordan V. C., Safe S. 3-Methylcholanthrene and other aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists directly activate estrogen receptor α. Cancer Res. 2006;66:2459–67. - PubMed
-
- Beischlag T. V., Perdew G. H. ER α-AHR-ARNT protein-protein interactions mediate estradiol-dependent transrepression of dioxin-inducible gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:21607–11. - PubMed
-
- Brosens J. J., Parker M. G. Gene expression: Oestrogen receptor hijacked. Nature. 2003;423:487–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

