Effects of digoxin on morbidity and mortality in diastolic heart failure: the ancillary digitalis investigation group trial
- PMID: 16864724
- PMCID: PMC2628473
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.628347
Effects of digoxin on morbidity and mortality in diastolic heart failure: the ancillary digitalis investigation group trial
Abstract
Background: About half of the 5 million heart failure patients in the United States have diastolic heart failure (clinical heart failure with normal or near-normal ejection fraction). Except for candesartan, no drugs have been tested in randomized clinical trials in these patients. Although digoxin was tested in an appreciable number of diastolic heart failure patients in the Digitalis Investigation Group ancillary trial, detailed findings from this important study have not previously been published.
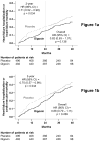
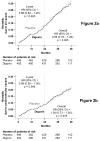
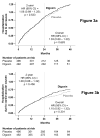
Methods and results: Ambulatory chronic heart failure patients (n = 988) with normal sinus rhythm and ejection fraction > 45% (median, 53%) from the United States and Canada (1991 to 1993) were randomly assigned to digoxin (n = 492) or placebo (n = 496). During follow-up with a mean length of 37 months, 102 patients (21%) in the digoxin group and 119 patients (24%) in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.82; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.63 to 1.07; P = 0.136) experienced the primary combined outcome of heart failure hospitalization or heart failure mortality. Digoxin had no effect on all-cause or cause-specific mortality or on all-cause or cardiovascular hospitalization. Use of digoxin was associated with a trend toward a reduction in hospitalizations resulting from worsening heart failure (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.59 to 1.04; P = 0.094) but also a trend toward an increase in hospitalizations for unstable angina (HR, 1.37; 95% CI, 0.99 to 1.91; P = 0.061).
Conclusions: In ambulatory patients with chronic mild to moderate diastolic heart failure and normal sinus rhythm receiving angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and diuretics, digoxin had no effect on natural history end points such as mortality and all-cause or cardiovascular hospitalizations.
Figures


Comment in
-
Does digoxin therapy affect outcome in patients with diastolic heart failure?Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007 Feb;4(2):70-1. doi: 10.1038/ncpcardio0765. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007. PMID: 17245399 No abstract available.
References
-
- American Heart Association. Heart disease and stroke statistics — 2005 update. Dallas, Texas: 2005.
-
- Zile MR, Gaasch WH, Carroll JD, Feldman MD, Aurigemma GP, Schaer GL, Ghali JK, Liebson PR. Heart failure with a normal ejection fraction: is measurement of diastolic function necessary to make the diagnosis of diastolic heart failure? Circulation. 2001 Aug 14;104(7):779–782. - PubMed
-
- Vasan RS, Larson MG, Benjamin EJ, Evans JC, Reiss CK, Levy D. Congestive heart failure in subjects with normal versus reduced left ventricular ejection fraction: prevalence and mortality in a population-based cohort. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 Jun;33(7):1948–1955. - PubMed
-
- Gottdiener JS, McClelland RL, Marshall R, Shemanski L, Furberg CD, Kitzman DW, Cushman M, Polak J, Gardin JM, Gersh BJ, Aurigemma GP, Manolio TA. Outcome of congestive heart failure in elderly persons: influence of left ventricular systolic function. The Cardiovascular Health Study. Ann Intern Med. 2002 Oct 15;137(8):631–639. - PubMed
-
- Redfield MM, Jacobsen SJ, Burnett JC, Jr, Mahoney DW, Bailey KR, Rodeheffer RJ. Burden of systolic and diastolic ventricular dysfunction in the community: appreciating the scope of the heart failure epidemic. JAMA. 2003 Jan 8;289(2):194–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

