Role of the Arabidopsis DNA glycosylase/lyase ROS1 in active DNA demethylation
- PMID: 16864782
- PMCID: PMC1544249
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0603563103
Role of the Arabidopsis DNA glycosylase/lyase ROS1 in active DNA demethylation
Abstract
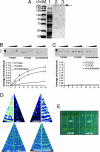
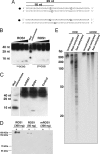
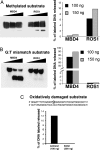
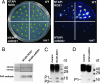
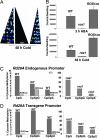
DNA methylation is a stable epigenetic mark for transcriptional gene silencing in diverse organisms including plants and many animals. In contrast to the well characterized mechanism of DNA methylation by methyltransferases, the mechanisms and function of active DNA demethylation have been controversial. Genetic evidence suggested that the DNA glycosylase domain-containing protein ROS1 of Arabidopsis is a putative DNA demethylase, because loss-of-function ros1 mutations cause DNA hypermethylation and enhance transcriptional gene silencing. We report here the biochemical characterization of ROS1 and the effect of its overexpression on the DNA methylation of target genes. Our data suggest that the DNA glycosylase activity of ROS1 removes 5-methylcytosine from the DNA backbone and then its lyase activity cleaves the DNA backbone at the site of 5-methylcytosine removal by successive beta- and delta-elimination reactions. Overexpression of ROS1 in transgenic plants led to a reduced level of cytosine methylation and increased expression of a target gene. These results demonstrate that ROS1 is a 5-methylcytosine DNA glycosylase/lyase important for active DNA demethylation in Arabidopsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
References
-
- Bird A. P., Wolffe A. P. Cell. 1999;99:451–454. - PubMed
-
- Rangwala S. H., Richards E. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004;14:686–691. - PubMed
-
- Chan S. W., Henderson I. R., Jacobsen S. E. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005;6:351–360. - PubMed
-
- Robertson K. D. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005;6:597–610. - PubMed
-
- Feinberg A. P., Ohlsson R., Henikoff S. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:21–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

