Cyclin D1 repression of nuclear respiratory factor 1 integrates nuclear DNA synthesis and mitochondrial function
- PMID: 16864783
- PMCID: PMC1518800
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0603363103
Cyclin D1 repression of nuclear respiratory factor 1 integrates nuclear DNA synthesis and mitochondrial function
Abstract
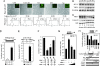
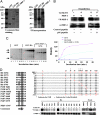
Cyclin D1 promotes nuclear DNA synthesis through phosphorylation and inactivation of the pRb tumor suppressor. Herein, cyclin D1 deficiency increased mitochondrial size and activity that was rescued by cyclin D1 in a Cdk-dependent manner. Nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF-1), which induces nuclear-encoded mitochondrial genes, was repressed in expression and activity by cyclin D1. Cyclin D1-dependent kinase phosphorylates NRF-1 at S47. Cyclin D1 abundance thus coordinates nuclear DNA synthesis and mitochondrial function.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures


References
-
- Shadel G. S., Clayton D. A. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997;66:409–435. - PubMed
-
- Larsson N. G., Wang J., Wilhelmsson H., Oldfors A., Rustin P., Lewandoski M., Barsh G. S., Clayton D. A. Nat. Genet. 1998;18:231–236. - PubMed
-
- Evans M. J., Scarpulla R. C. Genes Dev. 1990;4:1023–1034. - PubMed
-
- Scarpulla R. C. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2002;1576:1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

