Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 is a critical factor of stroke-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 16864802
- PMCID: PMC1518807
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0604400103
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 is a critical factor of stroke-reperfusion injury
Abstract
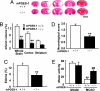
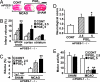
Although augmented prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) synthesis and accumulation have been demonstrated in the lesion sites of rodent transient focal ischemia models, the role of PGE(2) in neuronal survival has been controversial, showing both protective and toxic effects. Here we demonstrate the induction of microsomal PGE synthase 1 (mPGES-1), an inducible terminal enzyme for PGE(2) synthesis, in neurons, microglia, and endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex after transient focal ischemia. In mPGES-1 knockout (KO) mice, in which the postischemic PGE(2) production in the cortex was completely absent, the infarction, edema, apoptotic cell death, and caspase-3 activation in the cortex after ischemia were all reduced compared with those in wild-type (WT) mice. Furthermore, the behavioral neurological dysfunctions observed after ischemia in WT mice were significantly ameliorated in KO mice. The ameliorated symptoms observed in KO mice after ischemia were reversed to almost the same severity as WT mice by intracerebroventricular injection of PGE(2) into KO mice. Our observations suggest that mPGES-1 may be a critical determinant of postischemic neurological dysfunctions and a valuable therapeutic target for treatment of human stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures


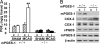

Similar articles
-
[The role of prostaglandin E2 in stroke-reperfusion injury].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013;133(9):947-54. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.13-00171. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013. PMID: 23995802 Review. Japanese.
-
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 contributes to ischaemic excitotoxicity through prostaglandin E2 EP3 receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jun;160(4):847-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00711.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20590584 Free PMC article.
-
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 are both required for ischaemic excitotoxicity.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Mar;159(5):1174-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00595.x. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20128796 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia-specific expression of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced prostaglandin E2 production.J Neurochem. 2005 Sep;94(6):1546-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03302.x. Epub 2005 Jul 5. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 16000148
-
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1: the inducible synthase for prostaglandin E2.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(3):114-7. doi: 10.1186/ar1748. Epub 2005 Apr 6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15899061 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Misoprostol Reverse Hippocampal Neuron Cyclooxygenase-2 Downstream Signaling Imbalance in Aluminum-Overload Rats.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(9):1006-16. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666160401114601. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 27033056 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based discovery of mPGES-1 inhibitors suitable for preclinical testing in wild-type mice as a new generation of anti-inflammatory drugs.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 26;8(1):5205. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23482-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29581541 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1 to develop drugs treating the inflammatory diseases.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Jan 15;13(1):391-419. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33527033 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effects, Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Potential of the Kv7/KCNQ Channel Opener QO-83 in Ischemic Stroke.Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Oct;16(5):1577-1593. doi: 10.1007/s12975-025-01329-1. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Transl Stroke Res. 2025. PMID: 39853651
-
Prostaglandins antagonistically control Bax activation during apoptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Mar;18(3):528-37. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.128. Epub 2010 Oct 22. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 20966963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lyden P. D., Grotta J. C., Levine S. R., Marler J. R., Frankel M. R., Brott T. G. Neurology. 1997;49:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Lyden P. D. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 1999;42:175–183. - PubMed
-
- Koistinaho J., Hokfelt T. NeuroReport. 1997;8:i–viii. - PubMed
-
- Dirnagl U., Iadecola C., Moskowitz M. A. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:391–397. - PubMed
-
- Barone F. C., Feuerstein G. Z. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:819–834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

