Multiplex bead array assay for detection of 25 soluble cytokines in blister fluid of patients with complex regional pain syndrome type 1
- PMID: 16864900
- PMCID: PMC1570387
- DOI: 10.1155/MI/2006/28398
Multiplex bead array assay for detection of 25 soluble cytokines in blister fluid of patients with complex regional pain syndrome type 1
Abstract
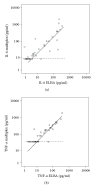
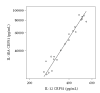
Inflammatory processes are known to be involved at least in the early phase of complex regional pain syndrome type 1 (CRPS1). Blister fluid obtained from the involved extremities displayed increased amounts of proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNFalpha compared with the noninvolved extremities. The aim of this paper is to investigate the involvement of mediators by measurement of several other cytokines using new detection techniques that enable multiple cytokine measurement in small samples. The use of a multiplex-25 bead array cytokine assay and Luminex technology enabled simultaneous measurement of representative (1) proinflammatory cytokines such as GM-CSF, IL-1beta, IL-1RA, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-alpha; (2) Th1/Th2 distinguishing cytokines IFN-gamma, IL-2, IL-2R, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10; (3) nonspecific acting cytokines IFN-alpha, IL-7, IL-12p40/p70, IL-13, IL-15, and IL-17; and (4) chemokines eotaxin, IP-10, MCP-1, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta, MIG, and RANTES. Although minimal detection levels are significantly higher in the bead array system than those in common ELISA assays, in blister fluid, IL-1RA, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-alpha, IL-12p40/p70, MCP-1, and MIP-1beta were detectable and increased in CRPS1 affected extremities. Levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha simultaneously measured by ELISA (Sanquin Compact kit) and by multiplex-25 bead array assay (Biosource) were highly correlated (r = 0.85, P < .001 for IL-6 and r = 0.88, P < .001 for TNF-alpha). Furthermore, IP-10 and eotaxin were detectable but diminished in CRPS1, whereas detectable amounts of IL-10 were similar in involved and noninvolved extremities. Multiplex bead array assays are useful systems to establish the involvement of cytokines in inflammatory processes by measurements in blister fluids of CRPS1. Ten representative cytokines were detectable. However, detection levels and amounts measured are at least 3 times higher in the multiplex-25 array assay than in the ELISA assays used simultaneously for the measurement of cytokines.
Figures
References
-
- Baron P, Schattschneider J, Binder A, Siebrecht D, Wasner G. Relation between sympathetic vasoconstrictor activity and pain and hyperalgesia in complex regional pain syndromes: a case-control study. The Lancet. 2002;359(9318):1655–1660. - PubMed
-
- Raja SN, Grabow TS. Complex regional pain syndrome I (reflex sympathetic dystrophy) Anesthesiology. 2002;96(5):1254–1260. - PubMed
-
- Veldman PHJM, Reynen HM, Arntz IE, Goris RJA. Signs and symptoms of reflex sympathetic dystrophy: prospective study of 829 patients. The Lancet. 1993;342(8878):1012–1016. - PubMed
-
- van de Beek W-JT, Schwartzman RJ, van Nes SI, Delhaas EM, van Hilten JJ. Diagnostic criteria used in studies of reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Neurology. 2002;58(4):522–526. - PubMed
-
- Bruehl S, Harden RN, Galer BS, et al. External validation of IASP diagnostic criteria for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome and proposed research diagnostic criteria. International Association for the Study of Pain. Pain. 1999;81(1-2):147–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

