Reversing gastric mucosal alterations during ethanol-induced chronic gastritis in rats by oral administration of Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage
- PMID: 16865772
- PMCID: PMC4087741
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i27.4318
Reversing gastric mucosal alterations during ethanol-induced chronic gastritis in rats by oral administration of Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage
Abstract
Aim: To study the effect of mucilage obtained from cladodes of Opuntia ficus-indica (Cactaceae) on the healing of ethanol-induced gastritis in rats.
Methods: Chronic gastric mucosa injury was treated with mucilage (5 mg/kg per day) after it was induced by ethanol. Lipid composition, activity of 5'-nucleotidase (a membrane-associated ectoenzyme) and cytosolic activities of lactate and alcohol dehydrogenases in the plasma membrane of gastric mucosa were determined. Histological studies of gastric samples from the experimental groups were included.
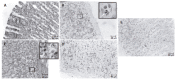
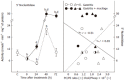
Results: Ethanol elicited the histological profile of gastritis characterized by loss of the surface epithelium and infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Phosphatidylcholine (PC) decreased and cholesterol content increased in plasma membranes of the gastric mucosa. In addition, cytosolic activity increased while the activity of alcohol dehydrogenases decreased. The administration of mucilage promptly corrected these enzymatic changes. In fact, mucilage readily accelerated restoration of the ethanol-induced histological alterations and the disturbances in plasma membranes of gastric mucosa, showing a univocal anti-inflammatory effect. The activity of 5'-nucleotidase correlated with the changes in lipid composition and the fluidity of gastric mucosal plasma membranes.
Conclusion: The beneficial action of mucilage seems correlated with stabilization of plasma membranes of damaged gastric mucosa. Molecular interactions between mucilage monosaccharides and membrane phospholipids, mainly PC and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), may be the relevant features responsible for changing activities of membrane-attached proteins during the healing process after chronic gastric mucosal damage.
Figures


References
-
- Bravo-Hollis H. Las cactáceas de México. Vol. I. Editorial UNAM. 1978.
-
- Demel RA, Dorrepaal E, Ebskamp MJ, Smeekens JC, de Kruijff B. Fructans interact strongly with model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1375:36–42. - PubMed
-
- Cárdenas A, Higuera-Ciapara I, Goycoolea FM. Rheology and aggregation of Cactus (Opuntia ficus- e indica) mucilagin solution. J PACD. 1997;2:152–157.
-
- Trachtenberg S, Mayer A. Biophysical properties of Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage. Phytochem. 1980;21:2835–2843.
-
- Medina-Torres L, Brito de la Fuente E, Torrestiana-Sánchez B, Katthain R. Rheological properties of the mucilage gum (Opuntia ficus-indica) Food Hydrocoll. 2000;14:417–424.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

