Duloxetine compared with fluoxetine and venlafaxine: use of meta-regression analysis for indirect comparisons
- PMID: 16867188
- PMCID: PMC1552056
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-244X-6-30
Duloxetine compared with fluoxetine and venlafaxine: use of meta-regression analysis for indirect comparisons
Abstract
Background: Data comparing duloxetine with existing antidepressant treatments is limited. A comparison of duloxetine with fluoxetine has been performed but no comparison with venlafaxine, the other antidepressant in the same therapeutic class with a significant market share, has been undertaken. In the absence of relevant data to assess the place that duloxetine should occupy in the therapeutic arsenal, indirect comparisons are the most rigorous way to go. We conducted a systematic review of the efficacy of duloxetine, fluoxetine and venlafaxine versus placebo in the treatment of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), and performed indirect comparisons through meta-regressions.
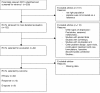
Methods: The bibliography of the Agency for Health Care Policy and Research and the CENTRAL, Medline, and Embase databases were interrogated using advanced search strategies based on a combination of text and index terms. The search focused on randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials involving adult patients treated for acute phase Major Depressive Disorder. All outcomes were derived to take account for varying placebo responses throughout studies. Primary outcome was treatment efficacy as measured by Hedge's g effect size. Secondary outcomes were response and dropout rates as measured by log odds ratios. Meta-regressions were run to indirectly compare the drugs. Sensitivity analysis, assessing the influence of individual studies over the results, and the influence of patients' characteristics were run.
Results: 22 studies involving fluoxetine, 9 involving duloxetine and 8 involving venlafaxine were selected. Using indirect comparison methodology, estimated effect sizes for efficacy compared with duloxetine were 0.11 [-0.14;0.36] for fluoxetine and 0.22 [0.06;0.38] for venlafaxine. Response log odds ratios were -0.21 [-0.44;0.03], 0.70 [0.26;1.14]. Dropout log odds ratios were -0.02 [-0.33;0.29], 0.21 [-0.13;0.55]. Sensitivity analyses showed that results were consistent.
Conclusion: Fluoxetine was not statistically different in either tolerability or efficacy when compared with duloxetine. Venlafaxine was significantly superior to duloxetine in all analyses except dropout rate. In the absence of relevant data from head-to-head comparison trials, results suggest that venlafaxine is superior compared with duloxetine and that duloxetine does not differentiate from fluoxetine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Lancet. 2018 Apr 7;391(10128):1357-1366. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32802-7. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Lancet. 2018. PMID: 29477251 Free PMC article.
-
Fluoxetine versus other types of pharmacotherapy for depression.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Oct 19;(4):CD004185. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004185.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 17;(7):CD004185. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004185.pub3. PMID: 16235353 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids for depression in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 24;11(11):CD004692. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004692.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34817851 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for the treatment of depression in people with cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 23;4(4):CD011006. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011006.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 31;3:CD011006. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011006.pub4. PMID: 29683474 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Antidepressants for the treatment of people with co-occurring depression and alcohol dependence.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 24;4(4):CD008581. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008581.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29688573 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy, tolerability, and acceptability of bupropion for major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials comparison with venlafaxine.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013 Sep 27;7:1053-62. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S46849. eCollection 2013. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013. PMID: 24101861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How should primary care doctors select which antidepressants to administer?Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2012 Aug;14(4):360-9. doi: 10.1007/s11920-012-0283-x. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2012. PMID: 22648236 Review.
References
-
- Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Mayle DA, Reid LR, Krushinski JH, Robertson DW. LY248686, a new inhibitor of serotonin and norepinephrine uptake. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1993;8:23–33. - PubMed
-
- Pitsikas N. Duloxetine. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2000;1:116–121. - PubMed
-
- Falissard B, Lothgren M, Perahia D, Garcia-Cebrian A. Meta-analyses of duloxetine in the treatment of MDD [Poster] presented at the 4th International Forum on Mood and Anxiety Disorders : abstract PO13, 19 Nov 2003. 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

