The response of RIF-1 fibrosarcomas to the vascular-disrupting agent ZD6126 assessed by in vivo and ex vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- PMID: 16867218
- PMCID: PMC1601935
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.06319
The response of RIF-1 fibrosarcomas to the vascular-disrupting agent ZD6126 assessed by in vivo and ex vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Abstract
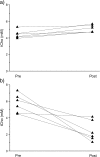
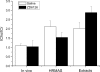
The response of radiation-induced fibrosarcoma 1 (RIF-1) tumors treated with the vascular-disrupting agent (VDA) ZD6126 was assessed by in vivo and ex vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) methods. Tumors treated with 200 mg/kg ZD6126 showed a significant reduction in total choline (tCho) in vivo 24 hours after treatment, whereas control tumors showed a significant increase in tCho. This response was investigated further within both ex vivo unprocessed tumor tissues and tumor tissue metabolite extracts. Ex vivo high-resolution magic angle spinning (HRMAS) and 1H MRS of metabolite extracts revealed a significant reduction in phosphocholine and glycerophosphocholine in biopsies of ZD6126-treated tumors, confirming in vivo tCho response. ZD6126-induced reduction in choline compounds is consistent with a reduction in cell membrane turnover associated with necrosis and cell death following disruption of the tumor vasculature. In vivo tumor tissue water diffusion and lactate measurements showed no significant changes in response to ZD6126. Spin-spin relaxation times (T2) of water and metabolites also remained unchanged. Noninvasive 1H MRS measurement of tCho in vivo provides a potential biomarker of tumor response to VDAs in RIF-1 tumors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of the vascular disrupting agent ZD6126 on interstitial fluid pressure and cell survival in tumors.Cancer Res. 2006 Feb 15;66(4):2074-80. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2046. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16489007
-
The vascular disrupting agent ZD6126 shows increased antitumor efficacy and enhanced radiation response in large, advanced tumors.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005 Jul 1;62(3):846-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.02.048. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. PMID: 15936569
-
Comparison of two vascular-disrupting agents at a clinically relevant dose in rodent liver tumors with multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers.Anticancer Drugs. 2012 Jan;23(1):12-21. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e328349dd60. Anticancer Drugs. 2012. PMID: 21857503
-
Biochemical characterization of breast tumors by in vivo and in vitro magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS).Biophys Rev. 2009 Mar;1(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s12551-008-0004-1. Epub 2009 Jan 17. Biophys Rev. 2009. PMID: 28510152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel roadmap connecting the 1H-MRS total choline resonance to all hallmarks of cancer following targeted therapy.Eur Radiol Exp. 2021 Jan 15;5(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s41747-020-00192-z. Eur Radiol Exp. 2021. PMID: 33447887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Applications of high-resolution magic angle spinning MRS in biomedical studies I-cell line and animal models.NMR Biomed. 2017 Jun;30(6):10.1002/nbm.3700. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3700. Epub 2017 Mar 16. NMR Biomed. 2017. PMID: 28301071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of breast tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with tomographic diffuse optical spectroscopy: case studies of tumor region-of-interest changes.Radiology. 2009 Aug;252(2):551-60. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2522081202. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Radiology. 2009. PMID: 19508985 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Response of Degarelix treatment in human prostate cancer monitored by HR-MAS 1H NMR spectroscopy.Metabolomics. 2016;12:120. doi: 10.1007/s11306-016-1055-0. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Metabolomics. 2016. PMID: 27429605 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo monitoring response to chemotherapy of human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma xenografts in SCID mice by 1H and 31P MRS.Acad Radiol. 2007 Dec;14(12):1531-9. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2007.07.012. Acad Radiol. 2007. PMID: 18035282 Free PMC article.
-
Murine liver implantation of radiation-induced fibrosarcoma: characterization with MR imaging, microangiography and histopathology.Eur Radiol. 2008 Jul;18(7):1422-30. doi: 10.1007/s00330-008-0904-2. Epub 2008 Mar 15. Eur Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18343928
References
-
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;43:175–203. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003;9:653–660. - PubMed
-
- Siemann DW, Chaplin DJ, Horsman MR. Vascular-targeting therapies for treatment of malignant disease. Cancer. 2004;100:2491–2499. - PubMed
-
- Tozer GM, Kanthou C, Baguley BC. Disrupting tumour blood vessels. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:423–435. - PubMed
-
- Blakey DC, Westwood FR, Walker M, Hughes GD, Davis PD, Ashton SE, Ryan AJ. Antitumor activity of the novel vascular targeting agent ZD6126 in a panel of tumor models. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:1974–1983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
