The open access advantage
- PMID: 16867971
- PMCID: PMC1550699
- DOI: 10.2196/jmir.8.2.e8
The open access advantage
Abstract
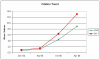
A study published today in PLoS Biology provides robust evidence that open-access articles are more immediately recognized and cited than non-OA articles. This editorial provides some additional follow up data from the most recent analysis of the same cohort in April 2006, 17 to 21 months after publication. These data suggest that the citation gap between open access and non-open access papers continues to widen. I conclude with the observation that the "open access advantage" has at least three components: (1) a citation count advantage (as a metric for knowledge uptake within the scientific community), (2) an end user uptake advantage, and (3) a cross-discipline fertilization advantage. More research is needed, and JMIR is inviting research on all aspects of open access. As the advantages for publishing open access from a researchers' point of view become increasingly clear, questions around the sustainability of open access journals remain. This journal is a living example that "lean publishing" models can create successful open access journals. Open source tools which have been developed by the Public Knowledge Project at the University of British Columbia with contributions from the Epublishing & Open Access group at the Centre for Global eHealth Innovation in Toronto are an alternative to hosting journals on commercial open access publisher sites.
Figures
Comment on
-
Citation advantage of open access articles.PLoS Biol. 2006 May;4(5):e157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040157. Epub 2006 May 16. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 16683865 Free PMC article.
-
Open access increases citation rate.PLoS Biol. 2006 May;4(5):e176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040176. Epub 2006 May 16. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 16683866 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
10 years experience with pioneering open access publishing in health informatics: the Journal of Medical Internet Research (JMIR).Stud Health Technol Inform. 2010;160(Pt 2):1329-33. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2010. PMID: 20841900
-
Does open access in ophthalmology affect how articles are subsequently cited in research?Ophthalmology. 2009 Aug;116(8):1425-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.12.052. Epub 2009 Jul 9. Ophthalmology. 2009. PMID: 19545905
-
Open access and global participation in science.Science. 2009 Feb 20;323(5917):1025. doi: 10.1126/science.1154562. Science. 2009. PMID: 19229029
-
[Biomedical publications in Spain on debate (I): state of neurological journals].Rev Neurol. 2007 Jan 1-15;44(1):32-42. Rev Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17199227 Review. Spanish.
-
Electronic theses and dissertations: a review of this valuable resource for nurse scholars worldwide.Int Nurs Rev. 2009 Jun;56(2):159-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1466-7657.2008.00703.x. Int Nurs Rev. 2009. PMID: 19646164 Review.
Cited by
-
Can tweets predict citations? Metrics of social impact based on Twitter and correlation with traditional metrics of scientific impact.J Med Internet Res. 2011 Dec 19;13(4):e123. doi: 10.2196/jmir.2012. J Med Internet Res. 2011. PMID: 22173204 Free PMC article.
-
Citation Advantage of Promoted Articles in a Cross-Publisher Distribution Platform: 36-Month Follow-up to a Randomized Controlled Trial.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Dec 10;23(12):e34051. doi: 10.2196/34051. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34890350 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Endoscopy as One of Leading Journals in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.Clin Endosc. 2015 Jul;48(4):312-6. doi: 10.5946/ce.2015.48.4.312. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Clin Endosc. 2015. PMID: 26240805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Which journals do primary care physicians and specialists access from an online service?J Med Libr Assoc. 2007 Jul;95(3):246-54. doi: 10.3163/1536-5050.95.3.246. J Med Libr Assoc. 2007. PMID: 17641754 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of free access to the scientific literature: a review of recent research.J Med Libr Assoc. 2011 Jul;99(3):208-17. doi: 10.3163/1536-5050.99.3.008. J Med Libr Assoc. 2011. PMID: 21753913 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eysenbach G. Citation Advantage of Open Access Articles. PLoS Biol. 2006;4(5):e157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040157. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0040157 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harnad S. Open Access Impact Advantage = EA + (AA) + (QB) + QA + (CA) + UA. [2006 May 10]. http://eprints.ecs.soton.ac.uk/12085/
-
- MacCallum CJ, Parthasarathy H. Open Access Increases Citation Rate. PLoS Biol. 2006;4(5):e176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040176. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0040176 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aronson Jeffrey K. Open access publishing: too much oxygen? BMJ. 2005 Apr 2;330(7494):759. doi: 10.1136/bmj.330.7494.759. http://bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=15802718330/7494/759 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Douw Karla, Vondeling Hindrik, Eskildsen Drea, Simpson Sue. Use of the Internet in scanning the horizon for new and emerging health technologies: a survey of agencies involved in horizon scanning. J Med Internet Res. 2003 Mar 31;5(1):e6. doi: 10.2196/jmir.5.1.e6. http://www.jmir.org/2003/1/e6/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous