Surgical treatment of spondylodiscitis in the cervical spine: a minimum 2-year follow-up
- PMID: 16868782
- PMCID: PMC2438571
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-006-0191-z
Surgical treatment of spondylodiscitis in the cervical spine: a minimum 2-year follow-up
Abstract
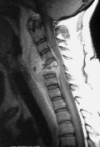
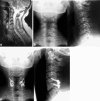
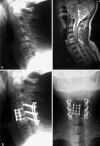
Cervical spine spondylodiscitis is a rare, but serious manifestation of spinal infection. We present a retrospective study of 20 consecutive patients between 01/1994 and 12/1999 treated because of cervical spondylodiscitis. Mean age at the time of treatment was 59.7 (range 34-81) years, nine of them female. In all cases, diagnosis had been established with a delay. All patients in this series underwent surgery such as radical debridement, decompression if necessary, autologous bone grafting and instrumentation. Surgery was indicated if a neurological deficit, symptoms of sepsis, epidural abscess formation with consecutive stenosis, instability or severe deformity were present. Postoperative antibiotic therapy was carried out for 8-12 weeks. Follow-up examinations were performed a mean of 37 (range 24-63) months after surgery. Healing of the inflammation was confirmed in all cases by laboratory, clinical and radiological parameters. Spondylodesis was controlled radiologically and could be achieved in all cases. One case showed a 15 degrees kyphotic angle in the proximal adjacent segment. Spontaneous bony bridging of the proximal adjacent segment was observed in one patient. In the other cases the adjacent segments radiologically showed neither fusion nor infection related changes. Preoperative neurological deficits improved in all cases. Residual neurological deficits persisted in three of eight cases. The results indicate that spondylodiscitis in cervical spine should be treated early and aggressive to avoid local and systemic complications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PEEK cage cervical ventral fusion in spondylodiscitis.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009 Nov;151(11):1537-41. doi: 10.1007/s00701-009-0486-z. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009. PMID: 19756355
-
Surgical results of long posterior fixation with short fusion in the treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis of the thoracic and lumbar spine: a retrospective study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 Dec 1;37(25):E1572-9. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31827399b8. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012. PMID: 22996263
-
Posterior fixation without debridement for vertebral body osteomyelitis and discitis.Neurosurg Focus. 2014 Aug;37(2):E6. doi: 10.3171/2014.6.FOCUS14142. Neurosurg Focus. 2014. PMID: 25081966
-
[Ventral interbody spondylodesis in injuries of the cervical spine. Indications, surgical technique and results].Zentralbl Chir. 1998;123(8):919-29. Zentralbl Chir. 1998. PMID: 9757537 Review. German.
-
Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012 Apr;16 Suppl 2:79-85. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22655486 Review.
Cited by
-
Cervical osteomyelitis in the setting of multiple comorbidities: a complex anatomical approach. Illustrative case.J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024 Oct 14;8(16):CASE24448. doi: 10.3171/CASE24448. Print 2024 Oct 14. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024. PMID: 39401465 Free PMC article.
-
PEEK cages as a potential alternative in the treatment of cervical spondylodiscitis: a preliminary report on a patient series.Eur Spine J. 2010 Jun;19(6):1004-9. doi: 10.1007/s00586-009-1265-5. Epub 2010 Jan 13. Eur Spine J. 2010. PMID: 20069319 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and surgical outcome in patients with cervical spondylodiscitis-a single-center retrospective case series of 24 patients.Front Surg. 2024 Jun 3;11:1292977. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1292977. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 38887314 Free PMC article.
-
Early fusion outcome after surgical treatment of single-level and multi-level pyogenic spondylodiscitis: experience at a level 1 center for spinal surgery-a single center cohort study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Feb 15;18(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03584-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36793045 Free PMC article.
-
Presentation and Outcomes After Medical and Surgical Treatment Versus Medical Treatment Alone of Spontaneous Infectious Spondylodiscitis: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis.Global Spine J. 2018 Dec;8(4 Suppl):49S-58S. doi: 10.1177/2192568218799058. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Global Spine J. 2018. PMID: 30574438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8015848', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8015848/'}]}
- Ditunno JF, Young W, Donovan WH, et al (1994) The international standards booklet for neurological and functional classification of spinal cord injury. Paraplegia 32:70–80 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2115262', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2115262/'}]}
- Endress C, Guyot DR, Fata J, Salciccioli G (1990) Cervical osteomyelitis due to IV heroin use: radiologic findings in 14 patient. AJR Am J Roentgenol 155: 333–335 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/BF01301428', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01301428'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC3454626', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3454626/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9258631', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9258631/'}]}
- Eysel P, Hopf C, Vogel I, et al (1997) Primary stable anterior instrumentation or dorsoventral spondylodesis in spondylodiscitis? Eur Spine J 6:152–157 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.spinee.2004.01.004', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2004.01.004'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15246297', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15246297/'}]}
- Fayazi AH, Ludwig SC, Dabbah M, Bryan Butler R, Gelb DE (2004) Preliminary results of staged anterior debridement and reconstruction using titanium mesh cages in the treatment of thoracolumbar vertebral osteomyelitis. Spine J 4:388–295 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00007632-200007010-00010', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-200007010-00010'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10870142', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10870142/'}]}
- Hadjipavlou AG, Mader JT, Necessary JT, et al (2000) Hematogenous pyogenic spinal infection and their surgical management. Spine 25:1668–1679 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

