Neuronal nitric oxide synthase immunopositivity in motoneurons of the rabbit's spinal cord after transient ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 16868818
- PMCID: PMC11520669
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-006-9087-z
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase immunopositivity in motoneurons of the rabbit's spinal cord after transient ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
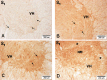
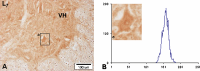
1. Motoneurons in the spinal cord are especially vulnerable to ischemic injury and selectively destroyed after transient ischemia. To evaluate the role of nitric oxide (NO) in the pathophysiology of the spinal cord ischemia, the expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) in the motoneurons of the lumbosacral spinal cord was examined in the rabbit model of transient abdominal aorta occlusion. 2. The aim of the present study was to find if there is any consensus between the duration of transient abdominal aorta occlusion, nNOS positivity of the motoneurons and neurological hind limb impairment. 3. According to the degree of neurological damage (i.e., from the group with almost no sign of damage to a group with fully developed paraplegia), the experimental animals were divided into three groups. The respective spinal cord segments of each experimental group were compared to the control group. 4. Spinal cord ischemia (15 min) was induced by Fogarty arterial embolectomy catheter occlusion of abdominal aorta with a reperfusion period of 7 days. On seventh day, the sections of lumbosacral segments were immunohistochemically treated and L1-L7, and S1-S2 segment sections were monitored using light microscopy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The vulnerability of nitrergic neurons to transient spinal cord ischemia: a quantitative immunohistochemical and histochemical study.J Mol Histol. 2012 Apr;43(2):203-13. doi: 10.1007/s10735-011-9386-7. Epub 2012 Jan 7. J Mol Histol. 2012. PMID: 22228218
-
Induction of neuronal and inducible nitric oxide synthase in the motoneurons of spinal cord following transient abdominal aorta occlusion in rats.J Surg Res. 1999 Dec;87(2):185-93. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1999.5754. J Surg Res. 1999. PMID: 10600348
-
Spatiotemporal alterations of the NO/NOS neuronal pools following transient abdominal aorta occlusion: morphological and biochemical studies in the rabbit.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006 Oct-Nov;26(7-8):1295-310. doi: 10.1007/s10571-006-9089-x. Epub 2006 Jun 20. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16786431 Free PMC article.
-
Peri-ischemic aminoguanidine fails to ameliorate neurologic and histopathologic outcome after transient spinal cord ischemia.J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2002 Jan;14(1):35-42. doi: 10.1097/00008506-200201000-00007. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2002. PMID: 11773821
-
Stem Cell Therapies for Restorative Treatments of Central Nervous System Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Mar;43(2):491-510. doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01204-9. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 35129759 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Region-specific sensitivity of the spinal cord to ischemia/reperfusion: the dynamic of changes in catalytic NOS activity.J Physiol Sci. 2009 Mar;59(2):97-103. doi: 10.1007/s12576-008-0013-7. Epub 2009 Jan 6. J Physiol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19340549 Free PMC article.
-
The vulnerability of nitrergic neurons to transient spinal cord ischemia: a quantitative immunohistochemical and histochemical study.J Mol Histol. 2012 Apr;43(2):203-13. doi: 10.1007/s10735-011-9386-7. Epub 2012 Jan 7. J Mol Histol. 2012. PMID: 22228218
References
-
- Ashwal, S., Tone, B., Tian, H. R., Cole, D. J., and Pearce, W. J. (1998). Core and penumbral nitric oxide synthase activity during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Stroke29:1037–1047. - PubMed
-
- Bolanos, J. P., and Almeida, A. (1999). Roles of nitric oxide in brain hypoxia-ischemia. Biochem. Biophys. Acta1411:415–436. - PubMed
-
- Bredt, D. S., and Snyder, S. H. (1992). Nitric oxide, a novel neuronal messenger. Neuron8:3–11. - PubMed
-
- Crawford, E. S., Crawford, J. L., Safi, H. J., Hess, K. R., and Brooks, B. (1986). Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms: Preoperative and intraoperative factors determining immediate and long-term results of operations in 605 patients. J. Vasc. Surg.3:389–404. - PubMed
-
- DeGirolami, U., and Zivin, J. A. (1982). Neuropathology of experimental spinal cord ischemia in the rabbit. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol.41:129–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

