Effect of ABCB1 (MDR1) haplotypes derived from G2677T/C3435T on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine in healthy subjects
- PMID: 16869811
- PMCID: PMC2000718
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2006.02733.x
Effect of ABCB1 (MDR1) haplotypes derived from G2677T/C3435T on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine in healthy subjects
Abstract
Aim: We aimed to investigate the effect of the ABCB1 gene on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
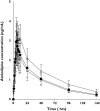
Methods: Based on polymorphisms of the ABCB1 gene at positions 2677 and 3435, 26 healthy male participants were divided into three groups: subjects with 2677GG/3435CC (n = 9), 2677GT/3435CT (n = 9) and 2677TT/3435TT (n = 8). After a single-dose administration of 5 mg amlodipine, plasma concentrations of amlodipine were measured and its pharmacokinetic characteristics were compared according to ABCB1 genotype.
Results: The area under the plasma concentration-time curve was significantly lower in subjects with 2677TT/3435TT (140.8 +/- 35.6 ng h(-1) ml(-1)) and 2677GT/3435CT (149.8 +/- 40.1 ng h(-1) ml(-1)) than in those with 2677GG/3435CC (208.6 +/- 39.2 ng h(-1) ml(-1)) [95% confidence interval (CI) on the difference, 2677GG/3435CC vs. 2677GT/3435CT 12.0, 105.6, P < 0.01; 2677GG/3435CC vs. 2677TT/3435TT 19.6, 116.0, P < 0.01; 2677GT/3435CT vs. 2677TT/3435TT - 39.2, 57.2, P > 0.05]. The peak plasma concentrations were highest in subjects with 2677GG/3435CC (3.8 +/- 0.5 ng ml(-1)), lower in subjects with 2677GT/3435CT (3.2 +/- 0.5 ng ml(-1)) and 2677TT/3435TT (2.7 +/- 0.5 ng ml(-1)) in rank and showed a significant difference between those with 2677GG/3435CC and with 2677TT/3435TT (95% CI on the difference 0.4, 2.0, P < 0.01). However, the oral clearance was higher in subjects with 2677TT/3435TT (37.7 +/- 10.2 l h(-1)) than in those with 2677GT/3435CT (35.7 +/- 9.9 l h(-1)) and with 2677GG/3435CC (24.8 +/- 5.4 l h(-1)) and exhibited a significant difference between ABCB1 genotype groups (95% CI on the difference, 2677GG/3435CC vs. 2677GT/3435CT - 21.5, - 0.3, P < 0.05; 2677GG/3435CC vs. 2677TT/3435TT - 23.8, - 2.0, P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Amlodipine pharmacokinetics was affected by the genetic polymorphisms of the ABCB1 gene in humans. These findings may provide a plausible explanation for interindividual variation in the disposition of amlodipine, although our study could not explain the exact mechanism(s) by which the polymorphic ABCB1 gene paradoxically reduces the plasma levels of amlodipine. Further evaluation is thus warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of ABCB1 gene polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of verapamil among healthy Chinese Han ethnic subjects.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Sep;68(3):395-401. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03467.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19740397 Free PMC article.
-
A variant 2677A allele of the MDR1 gene affects fexofenadine disposition.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Nov;76(5):418-27. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2004.08.002. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15536457
-
Effect of itraconazole on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of fexofenadine in relation to the MDR1 genetic polymorphism.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Aug;78(2):191-201. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2005.04.012. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 16084853 Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of ABCB1 gene polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of azithromycin among healthy Chinese Han ethnic subjects.Pharmacol Rep. 2009 Sep-Oct;61(5):843-50. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(09)70140-9. Pharmacol Rep. 2009. PMID: 19904007
-
Effect of ABCB1 3435C>T Genetic Polymorphism on Pharmacokinetic Variables of Tacrolimus in Adult Renal Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Ther. 2020 Oct;42(10):2049-2065. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2020.07.016. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Clin Ther. 2020. PMID: 32888708
Cited by
-
Pharmacogenomics-based individualized treatment of hypertension in preterm infants: A case report and review of the literature.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Oct 26;11(30):7440-7449. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7440. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37969466 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of ABCB1 gene polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of verapamil among healthy Chinese Han ethnic subjects.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Sep;68(3):395-401. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03467.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19740397 Free PMC article.
-
Bioequivalence evaluation of two amlodipine salts, besylate and orotate, each in a fixed-dose combination with olmesartan in healthy subjects.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jun 2;9:2811-7. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S82820. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26082611 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association of variants in the ABCB1, CYP2C19 and CYP2C9 genes for Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy.Neurol Sci. 2024 Apr;45(4):1635-1643. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-07124-w. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 37875597
-
Effect of MDR1 C3435T polymorphism on lansoprazole in healthy Japanese subjects.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;65(6):593-600. doi: 10.1007/s00228-009-0625-8. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19238367
References
-
- Ieiri I, Takane H, Otsubo K. The MDR1 (ABCB1) gene polymorphism and its clinical implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2004;43:553–76. - PubMed
-
- Eichelbaum M, Fromm MF, Schwab M. Clinical aspects of the MDR1 (ABCB1) gene polymorphism. Ther Drug Monit. 2004;26:180–5. - PubMed
-
- Park JY, Kim KA, Lee GS, Park PW, Kim SL, Lee YS, Lee YW, Shin EK. Randomized, open-label, two-period crossover comparison of the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of two amlodipine formulations in healthy adult male Korean subjects. Clin Ther. 2004;26:715–23. - PubMed
-
- Abernethy DR. The pharmacokinetic profile of amlodipine. Am Heart J. 1989;118:1100–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources