Cellular immune reaction in the pancreas is induced by constitutively active IkappaB kinase-2
- PMID: 16870717
- PMCID: PMC1856776
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2005.084665
Cellular immune reaction in the pancreas is induced by constitutively active IkappaB kinase-2
Abstract
Background: Activation of the nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) system is a major event in acute and chronic inflammatory processes. NF-kappaB cascades are comprised of IkappaB kinases, IkappaBs and NF-kappaB dimers. Little is known of the individual roles of these proteins in organ specific inflammation. The aim of the present study was to analyse the consequences of ectopic IkappaB kinase-2 (IKK2) activation in the pancreas of mice.
Methods: Transgenic mice were generated using an inducible genetic system (tet system) to conditionally overexpress a gain of function mutant of IKK2 (tetO-IKK2-EE) in the pancreas. To achieve transgene expression in the pancreas, these animals were crossed with CMV-rtTA mice that are known to express the rtTA protein in the pancreas.
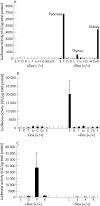
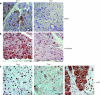
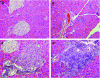
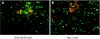
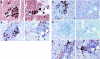
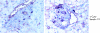
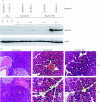
Results: In these double transgenic animals, doxycycline treatment induced expression of IKK2-EE (IKK2(CA)) in pancreatic acinar cells resulting in moderate activation of the IkappaB kinase complex, as measured by the immune complex kinase assay, and up to 200-fold activation of the transgene expression cassette, as detected by luciferase assay. IKK2(CA) expression in the pancreas had a mosaic appearance. Ectopic IKK2(CA) mostly activated the classical NF-kappaB pathway. The activation level of the NF-kappaB cascade induced by IKK2(CA) was considerably lower compared with that observed after supramaximal caerulein stimulation but still led to the formation of leucocyte infiltrates first observed after 4 weeks of doxycycline stimulation with a maximum after 8-12 weeks. The infiltrates were mainly composed of B lymphocytes and macrophages. Increased mRNA levels of tumour necrosis factor alpha and RANTES were detected in pancreatic acinar cells. However, only minor damage to pancreatic tissue was observed. A combination of supramaximal caerulein stimulation with induction of IKK2(CA) caused increased tissue damage compared with either IKK2(CA) or caerulein alone.
Conclusions: Our observations suggest that the role of IKK2 activation in pancreatic acini is to induce leucocyte infiltration, but at a moderate level of activation it is not sufficient to induce pancreatic damage in mice. The IKK2(CA) induced infiltrations resemble those observed in autoimmune pancreatitis, indicating a role for IKK2/NF-kappaB in this disease. IKK2(CA) in pancreatic acinar cells increases tissue damage of secretagogue induced experimental pancreatitis underlining the proinflammatory role of the IKK/NF-kappaB pathway in this disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interest: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Constitutive IKK2 activation in acinar cells is sufficient to induce pancreatitis in vivo.J Clin Invest. 2007 Jun;117(6):1502-13. doi: 10.1172/JCI30876. Epub 2007 May 24. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17525799 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of nuclear factor-κB in acinar cells increases the severity of pancreatitis in mice.Gastroenterology. 2013 Jan;144(1):202-10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.09.059. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23041324 Free PMC article.
-
Water immersion stress prevents caerulein-induced pancreatic acinar cell nf-kappa b activation by attenuating caerulein-induced intracellular Ca2+ changes.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 1;276(22):18742-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009721200. Epub 2001 Feb 15. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278554
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
IkappaB kinase beta (IKKbeta/IKK2/IKBKB)--a key molecule in signaling to the transcription factor NF-kappaB.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008 Apr;19(2):157-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2008.01.006. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008. PMID: 18308615 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling in cerulein pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 14;20(46):17324-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17324. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25516643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoimmune pancreatitis-related diabetes: quantitative analysis of endocrine islet cells and inflammatory infiltrate.Virchows Arch. 2010 Sep;457(3):329-36. doi: 10.1007/s00428-010-0948-y. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Virchows Arch. 2010. PMID: 20632032
-
Intra-acinar trypsinogen activation mediates early stages of pancreatic injury but not inflammation in mice with acute pancreatitis.Gastroenterology. 2011 Dec;141(6):2210-2217.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.08.033. Epub 2011 Aug 27. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21875495 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic mechanisms of acute pancreatitis.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012 Sep;28(5):507-15. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e3283567f52. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22885948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics, Cell Biology, and Pathophysiology of Pancreatitis.Gastroenterology. 2019 May;156(7):1951-1968.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.11.081. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30660731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rothwarf D M, Karin M. The NF‐kappa B activation pathway: a paradigm in information transfer from membrane to nucleus. Sci STKE 19991999RE1 - PubMed
-
- Senftleben U, Karin M. The IKK/NF‐kappaB pathway. Crit Care Med 200230S18–S26. - PubMed
-
- Israel A. The IKK complex: an integrator of all signals that activate NF‐kappaB? Trends Cell Biol 200010129–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases