Identification of single-point mutations in mycobacterial 16S rRNA sequences by confocal single-molecule fluorescence spectroscopy
- PMID: 16870719
- PMCID: PMC1540729
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl495
Identification of single-point mutations in mycobacterial 16S rRNA sequences by confocal single-molecule fluorescence spectroscopy
Abstract
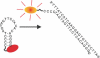
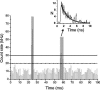
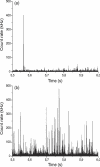
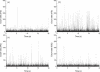
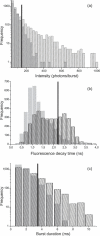
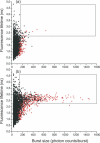
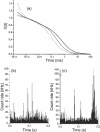
We demonstrate the specific identification of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) responsible for rifampicin resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis applying fluorescently labeled DNA-hairpin structures (smart probes) in combination with single-molecule fluorescence spectroscopy. Smart probes are singly labeled hairpin-shaped oligonucleotides bearing a fluorescent dye at the 5' end that is quenched by guanosine residues in the complementary stem. Upon hybridization to target sequences, a conformational change occurs, reflected in a strong increase in fluorescence intensity. An excess of unlabeled ('cold') oligonucleotides was used to prevent the formation of secondary structures in the target sequence and thus facilitates hybridization of smart probes. Applying standard ensemble fluorescence spectroscopy we demonstrate the identification of SNPs in PCR amplicons of mycobacterial rpoB gene fragments with a detection sensitivity of 10(-8) M. To increase the detection sensitivity, confocal fluorescence microscopy was used to observe fluorescence bursts of individual smart probes freely diffusing through the detection volume. By measuring burst size, burst duration and fluorescence lifetime for each fluorescence burst the discrimination accuracy between closed and open (hybridized) smart probes could be substantially increased. The developed technique enables the identification of SNPs in 10(-11) M solutions of PCR amplicons from M.tuberculosis in only 100 s.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Species-specific identification of mycobacterial 16S rRNA PCR amplicons using smart probes.Anal Chem. 2005 Nov 15;77(22):7195-203. doi: 10.1021/ac051447z. Anal Chem. 2005. PMID: 16285666
-
DNA-probes for the highly sensitive identification of single nucleotide polymorphism using single-molecule spectroscopy.FEBS Lett. 2007 Apr 17;581(8):1644-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.03.031. Epub 2007 Mar 20. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17399707
-
Probes for detection of specific DNA sequences at the single-molecule level.Anal Chem. 2000 Aug 15;72(16):3717-24. doi: 10.1021/ac000024o. Anal Chem. 2000. PMID: 10959954
-
Single-Labeled Oligonucleotides Showing Fluorescence Changes Upon Hybridization with Target Nucleic Acids.Molecules. 2018 Jan 8;23(1):124. doi: 10.3390/molecules23010124. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29316733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of hydrolysis and hairpin probes in real-time PCR.Mol Biotechnol. 2003 Nov;25(3):267-74. doi: 10.1385/MB:25:3:267. Mol Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 14668539 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecularly resolved label-free sensing of single nucleobase mismatches by interfacial LNA probes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 May 5;44(8):3739-49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw197. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27025649 Free PMC article.
-
Tunable blinking kinetics of cy5 for precise DNA quantification and single-nucleotide difference detection.Biophys J. 2008 Jul;95(2):729-37. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.127530. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18424494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Telenti A., Imboden P., Marchesi F., Lowrie D., Cole S., Colston M.J., Matter L., Schopfer K., Bodmer T. Detection of Rifampicin-resistance mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lancet. 1993;341:647–650. - PubMed
-
- Mokrousov I., Otten T., Vyazovaya A., Limeschenko E., Filipenko M.L., Sola C., Rastogi N., Steklova L., Vyshnevskiy B., Narvskaya O. PCR-based methodology for detecting Multidrug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Beijing Family circulating in Russia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003;22:342–348. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho W.S., Spindola de Miranda S., Costa K.M., Araujo J.G., Augusto C.J., Pesquero J.B., Pesquero J.L., Gomes M.A. Low-stringency single-specific-primer PCR as a tool for detection of mutations in the rpoB gene of rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003;41:3384–3386. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

