Modulation of h-channels in hippocampal pyramidal neurons by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 16870744
- PMCID: PMC6674228
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2069-06.2006
Modulation of h-channels in hippocampal pyramidal neurons by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
Abstract
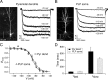
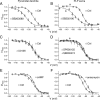
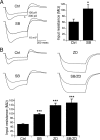
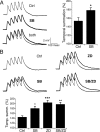
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels (h-channels; I(h); HCN) modulate intrinsic excitability in hippocampal and neocortical pyramidal neurons, among others. Whereas I(h) mediated by the HCN2 isoform is regulated by cAMP, there is little known about kinase modulation of I(h), especially for the HCN1 isoform predominant in pyramidal neurons. We used a computational method to identify a novel kinase modulator of h-channels, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK). Inhibition of p38 MAPK in hippocampal pyramidal neurons caused a approximately 25 mV hyperpolarization of I(h) voltage-dependent activation. This downregulation of I(h) produced hyperpolarization of resting potential, along with increased input resistance and temporal summation of excitatory inputs. Activation of p38 MAPK caused a approximately 11 mV depolarizing shift in I(h) activation, along with depolarized resting potential, and decreased input resistance and temporal summation. Inhibition of related MAPKs, ERK1/2 (extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2) and JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase), produced no effect on I(h). These results show that p38 MAPK is a strong modulator of h-channel biophysical properties and may deserve additional exploration as a link between altered I(h) and pathological conditions such as epilepsy.
Figures


Comment in
-
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase: a novel modulator of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels and neuronal excitability.J Neurosci. 2006 Nov 1;26(44):11253-4. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.3852-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17083163 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Activity-dependent regulation of h channel distribution in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 9;282(45):33168-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703736200. Epub 2007 Sep 11. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17848552 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C bidirectionally modulates Ih and hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel surface expression in hippocampal pyramidal neurons.J Physiol. 2015 Jul 1;593(13):2779-92. doi: 10.1113/JP270453. Epub 2015 May 22. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25820761 Free PMC article.
-
Kv7/KCNQ/M and HCN/h, but not KCa2/SK channels, contribute to the somatic medium after-hyperpolarization and excitability control in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cells.J Physiol. 2005 Aug 1;566(Pt 3):689-715. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.086835. Epub 2005 May 12. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15890705 Free PMC article.
-
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase: a novel modulator of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels and neuronal excitability.J Neurosci. 2006 Nov 1;26(44):11253-4. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.3852-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17083163 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Neurophysiology of HCN channels: from cellular functions to multiple regulations.Prog Neurobiol. 2014 Jan;112:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Prog Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24184323 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced Hyperpolarization-Activated Current Contributes to Enhanced Intrinsic Excitability in Cultured Hippocampal Neurons from PrP(-/-) Mice.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Mar 24;10:74. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00074. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27047338 Free PMC article.
-
The fast and slow ups and downs of HCN channel regulation.Channels (Austin). 2010 May-Jun;4(3):215-31. doi: 10.4161/chan.4.3.11630. Channels (Austin). 2010. PMID: 20305382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Inhibition of p38 MAPK as a Potential Strategy for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2017 Aug 2;22(8):1287. doi: 10.3390/molecules22081287. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28767069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabinoid Control of Learning and Memory through HCN Channels.Neuron. 2016 Mar 2;89(5):1059-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.023. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 26898775 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-dependent regulation of h channel distribution in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 9;282(45):33168-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703736200. Epub 2007 Sep 11. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17848552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arima H, Yamamoto N, Sobue K, Umenishi F, Tada T, Katsuya H, Asai K (2003). Hyperosmolar mannitol simulates expression of aquaporins 4 and 9 through a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway in rat astrocytes. J Biol Chem 278:44525–44534. - PubMed
-
- Beaumont V, Zhong N, Froemke RC, Ball RW, Zucker RS (2002). Temporal synaptic tagging by Ih activation and actin: involvement in long-term facilitation and cAMP-induced synaptic enhancement. Neuron 33:601–613. - PubMed
-
- Bolshakov VY, Carboni L, Cobb MH, Siegelbaum SA, Belardetti F (2000). Dual MAP kinase pathways mediate opposing forms of long-term plasticity at CA3-CA1 synapses. Nat Neurosci 3:1107–1112. - PubMed
-
- Bullis JB, Jones TD, Poolos NP (2004). h-channel distribution in “pyramidal-like” principal neurons in stratum radiatum of hippocampus differs from pyramidal neurons. Soc Neurosci Abstr 29:52.59.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
