Novel nonnucleoside inhibitors that select nucleoside inhibitor resistance mutations in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase
- PMID: 16870771
- PMCID: PMC1538665
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00127-06
Novel nonnucleoside inhibitors that select nucleoside inhibitor resistance mutations in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase
Abstract
Mutations in and around the catalytic site of the reverse transcriptase (RT) of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) are associated with resistance to nucleoside RT inhibitors (NRTIs), whereas changes in the hydrophobic pocket of the RT are attributed to nonnucleoside RT inhibitor (NNRTI) resistance. In this study, we report a novel series of nonnucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1, exemplified by VRX-329747 and VRX-413638, which inhibit both NNRTI- and NRTI-resistant HIV-1 isolates. Enzymatic studies indicated that these compounds are HIV-1 RT inhibitors. Surprisingly, however, following prolonged (6 months) tissue culture selection, this series of nonnucleoside inhibitors did not select NNRTI-resistant mutations in HIV-1 RT. Rather, four mutations (M41L, A62T/V, V118I, and M184V) known to cause resistance to NRTIs and two additional novel mutations (S68N and G112S) adjacent to the catalytic site of the enzyme were selected. Although the M184V mutation appears to be the initial mutation to establish resistance, this mutation alone confers only a two- to fourfold decrease in susceptibility to VRX-329747 and VRX-413638. At least two additional mutations must accumulate for significant resistance. Moreover, while VRX-329747-selected viruses are resistant to lamivudine and emtricitabine due to the M184V mutation, they remain susceptible to zidovudine, stavudine, dideoxyinosine, abacavir, tenofovir, and efavirenz. These results directly demonstrate that VRX-329747 and VRX-413638 are novel nonnucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 RT with the potential to augment current therapies.
Figures
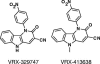

Similar articles
-
Mutational patterns in the HIV genome and cross-resistance following nucleoside and nucleotide analogue drug exposure.Antivir Ther. 2001;6 Suppl 3:25-44. Antivir Ther. 2001. PMID: 11678471 Review.
-
In vitro characterization of a simian immunodeficiency virus-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) chimera expressing HIV type 1 reverse transcriptase to study antiviral resistance in pigtail macaques.J Virol. 2004 Dec;78(24):13553-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.24.13553-13561.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15564466 Free PMC article.
-
NNRTI-selected mutations at codon 190 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase decrease susceptibility to stavudine and zidovudine.Antiviral Res. 2007 Nov;76(2):99-103. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2007.06.002. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Antiviral Res. 2007. PMID: 17640745
-
Thymidine analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitors resistance mutations profiles and association to other nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors resistance mutations observed in the context of virological failure.J Med Virol. 2004 Jan;72(1):162-5. doi: 10.1002/jmv.10550. J Med Virol. 2004. PMID: 14635026
-
K65R, TAMs and tenofovir.AIDS Rev. 2004 Jan-Mar;6(1):22-33. AIDS Rev. 2004. PMID: 15168738 Review.
Cited by
-
Pronounced Inhibition Shift from HIV Reverse Transcriptase to Herpetic DNA Polymerases by Increasing the Flexibility of α-Carboxy Nucleoside Phosphonates.J Med Chem. 2015 Oct 22;58(20):8110-27. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01180. Epub 2015 Oct 9. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26450273 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis of HIV-1 Inhibition by Nucleotide-Competing Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor INDOPY-1.J Med Chem. 2019 Nov 14;62(21):9996-10002. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01289. Epub 2019 Oct 25. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31603676 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations M184V and Y115F in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase discriminate against "nucleotide-competing reverse transcriptase inhibitors".J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 31;283(44):29904-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804882200. Epub 2008 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18728003 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of a quaternary complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with a nucleotide-competing inhibitor and its ATP enhancer.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 14;288(24):17336-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.433441. Epub 2013 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23598281 Free PMC article.
-
A novel nonnucleoside analogue that inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates resistant to current nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Feb;51(2):429-37. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01032-06. Epub 2006 Nov 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17116677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Althaus, I. W., J. J. Chou, A. J. Gonzales, M. R. Deibel, K. C. Chou, F. J. Kezdy, D. L. Romero, J. R. Palmer, R. C. Thomas, P. A. Aristoff, W. G. Tarpley, and F. Reusser. 1993. Kinetic studies with the non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor U-88204E. Biochemistry 32:6548-6554. - PubMed
-
- Antinori, A., M. Zaccarelli, A. Cingolani, F. Forbici, M. G. Rizzo, M. P. Trotta, S. Di Giambenedetto, P. Narciso, A. Ammassari, E. Girardi, A. De Luca, and C. F. Perno. 2002. Cross-resistance among nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors limits recycling efavirenz after nevirapine failure. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 18:835-838. - PubMed
-
- Auwerx, J., M. Stevens, A. R. Van Rompay, L. E. Bird, J. Ren, E. De Clercq, B. Oberg, D. K. Stammers, A. Karlsson, and J. Balzarini. 2004. The phenylmethylthiazolylthiourea nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitor MSK-076 selects for a resistance mutation in the active site of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 RT. J. Virol. 78:7427-7437. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bacheler, L., S. Jeffrey, G. Hanna, R. D'Aquila, L. Wallace, K. Logue, B. Cordova, K. Hertogs, B. Larder, R. Buckery, D. Baker, K. Gallagher, H. Scarnati, R. Tritch, and C. Rizzo. 2001. Genotypic correlates of phenotypic resistance to efavirenz in virus isolates from patients failing nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor therapy. J. Virol. 75:4999-5008. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bacheler, L. T., E. D. Anton, P. Kudish, D. Baker, J. Bunville, K. Krakowski, L. Bolling, M. Aujay, X. V. Wang, D. Ellis, M. F. Becker, A. L. Lasut, H. J. George, D. R. Spalding, G. Hollis, and K. Abremski. 2000. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutations selected in patients failing efavirenz combination therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:2475-2484. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

