A novel algorithm for comprehensive fetal echocardiography using 4-dimensional ultrasonography and tomographic imaging
- PMID: 16870887
- PMCID: PMC1800884
- DOI: 10.7863/jum.2006.25.8.947
A novel algorithm for comprehensive fetal echocardiography using 4-dimensional ultrasonography and tomographic imaging
Abstract
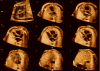
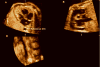
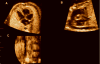
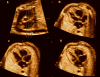
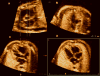
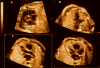
Objective: Tomographic ultrasound imaging (TUI) is a new display modality that allows simultaneous visualization of up to 8 parallel anatomic planes. This study was designed to determine the role of a novel algorithm combining spatiotemporal image correlation and TUI to visualize standard fetal echocardiographic planes.
Methods: Volume data sets from fetuses with and without congenital heart defects (CHDs) were examined with a novel algorithm that allows simultaneous visualization of the 3-vessel and trachea view, the 4-chamber view, and outflow tracts. Visualization rates for these planes as well as the ductal arch and 5-chamber view were calculated.
Results: (1) Two hundred twenty-seven volume data sets from fetuses without (n = 138) and with (n = 14) CHDs were reviewed; (2) among fetuses without CHDs, the 4-chamber view, 5-chamber view, ductal arch, 3-vessel and trachea view, left outflow tract, and short axis of the aorta were visualized in 99% (193/195), 96.9% (189/195), 98.5% (192/195), 88.2% (172/195), 93.3% (182/195), and 87.2% (170/195) of the volume data sets, respectively; (3) these views were visualized in 85% (17/20), 80% (16/20), 65% (13/20), 55% (11/20), 55% (11/20), and 70% (14/20) of the volume data sets, respectively, from fetuses with CHDs; and (4) simultaneous visualization of the short axis of the aorta, 3-vessel and trachea view, left outflow tract, and 4-chamber view was obtained in 78% (152/195) of the volume data sets from fetuses without CHDs and in 40% (8/20) of those with CHDs.
Conclusions: The 3-vessel and trachea view, the 4-chamber view, and both outflow tracts can be simultaneously visualized using a novel algorithm combining spatiotemporal image correlation and TUI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Four-dimensional ultrasonography of the fetal heart using a novel Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging display.J Perinat Med. 2006;34(1):39-55. doi: 10.1515/JPM.2006.006. J Perinat Med. 2006. PMID: 16489885 Free PMC article.
-
Four-chamber view and 'swing technique' (FAST) echo: a novel and simple algorithm to visualize standard fetal echocardiographic planes.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011 Apr;37(4):423-31. doi: 10.1002/uog.8840. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011. PMID: 20878671 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the sagittal view of the ductal arch in identification of fetuses with conotruncal anomalies using 4-dimensional ultrasonography.J Ultrasound Med. 2007 Sep;26(9):1181-8; quiz 1189-90. doi: 10.7863/jum.2007.26.9.1181. J Ultrasound Med. 2007. PMID: 17715312 Free PMC article.
-
Contemporary clinical applications of spatio-temporal image correlation in prenatal diagnosis.Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2011 Apr;23(2):94-102. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0b013e328342ef38. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2011. PMID: 21178772 Review.
-
[Fetal echocardiography: part II--anomalies of the four-chamber view].Akush Ginekol (Sofiia). 2009;48(6):27-37. Akush Ginekol (Sofiia). 2009. PMID: 20225494 Review. Bulgarian.
Cited by
-
Assessment of the fetal heart at 12-14 weeks of pregnancy using B-mode, color Doppler, and spatiotemporal image correlation via abdominal and vaginal ultrasonography.Pediatr Cardiol. 2013 Oct;34(7):1577-82. doi: 10.1007/s00246-013-0686-4. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Pediatr Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23479309
-
Anomalous Fusion of Right Pulmonary Artery to Aortic Arch: Case Report of a Rare and Fatal Congenital Malformation in a Newborn and a Literature Review.Am J Case Rep. 2018 Nov 28;19:1416-1421. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.909749. Am J Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30482890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repeatability and reproducibility of fetal cardiac ventricular volume calculations using spatiotemporal image correlation and virtual organ computer-aided analysis.J Ultrasound Med. 2009 Oct;28(10):1301-11. doi: 10.7863/jum.2009.28.10.1301. J Ultrasound Med. 2009. PMID: 19778875 Free PMC article.
-
A Prospective Study of the Use of Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) to Obtain Standard Fetal Echocardiography Views.Fetal Diagn Ther. 2017;41(2):89-99. doi: 10.1159/000446982. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2017. PMID: 27309391 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal echocardiography.Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2009 Feb;19(1):60-8. doi: 10.4103/0971-3026.44524. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2009. PMID: 19774143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boneva RS, Botto LD, Moore CA, et al. Mortality associated with congenital heart defects in the United States: trends and racial disparities, 1979–1997. Circulation. 2001;103:2376–2381. - PubMed
-
- Stoll C, Alembik Y, Dott B, Roth PM, De Geeter B. Evaluation of prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease. Prenat Diagn. 1993;13:453–461. - PubMed
-
- Crane JP, LeFevre ML, Winborn RC, et al. A randomized trial of prenatal ultrasonographic screening: impact on the detection, management, and outcome of anomalous fetuses. The RADIUS Study Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;171:392–399. - PubMed
-
- Rustico MA, Benettoni A, D'Ottavio G, et al. Fetal heart screening in low-risk pregnancies. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1995;6:313–319. - PubMed
-
- Buskens E, Grobbee DE, Frohn-Mulder IME, et al. Efficacy of Routine Fetal Ultrasound Screening for Congenital Heart Disease in Normal Pregnancy. Circulation. 1996;94:67–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

