Two distinct binding modes of a protein cofactor with its target RNA
- PMID: 16872630
- PMCID: PMC2633024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.06.048
Two distinct binding modes of a protein cofactor with its target RNA
Abstract
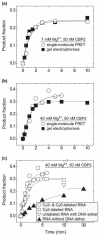
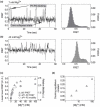
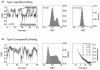
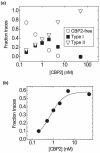
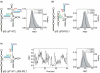
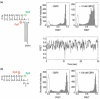
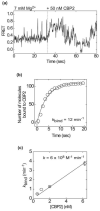
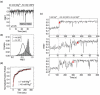
Like most cellular RNA enzymes, the bI5 group I intron requires binding by a protein cofactor to fold correctly. Here, we use single-molecule approaches to monitor the structural dynamics of the bI5 RNA in real time as it assembles with its CBP2 protein cofactor. These experiments show that CBP2 binds to the target RNA in two distinct modes with apparently opposite effects: a "non-specific" mode that forms rapidly and induces large conformational fluctuations in the RNA, and a "specific" mode that forms slowly and stabilizes the native RNA structure. The bI5 RNA folds though multiple pathways toward the native state, typically traversing dynamic intermediate states induced by non-specific binding of CBP2. These results suggest that the protein cofactor-assisted RNA folding involves sequential non-specific and specific protein-RNA interactions. The non-specific interaction potentially increases the local concentration of CBP2 and the number of conformational states accessible to the RNA, which may promote the formation of specific RNA-protein interactions.
Figures


References
-
- Gesteland RF, Cech TR, Atkins JF. The RNA world. Second Edition Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; New York: 1999.
-
- Pan J, Woodson SA. Folding intermediates of a self-splicing RNA: Mispairing of the catalytic core. J. Mol. Biol. 1998;280:597–609. - PubMed
-
- Pan T, Sosnick TR. Intermediates and kinetics traps in the folding of a large ribozyme revealed by circular dichroism and UV absorbance spectroscopies and catalytic activity. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997;4:931–938. - PubMed
-
- Russell R, Herschlag D. New pathways in folding of the Tetrahymena group I RNA enzyme. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;291:1155–1167. - PubMed
-
- Treiber DK, Rook MS, Zarrinkar PP, Williamson JR. Kinetic intermediates trapped by native interactions in RNA folding. Science. 1998;279:1943–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

