Obesity and its therapy: from genes to community action
- PMID: 16873005
- PMCID: PMC2771638
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pcl.2006.05.011
Obesity and its therapy: from genes to community action
Abstract
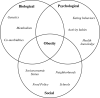
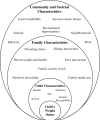
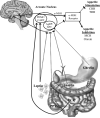
Like many diseases, the causes of obesity are complex, and their investigation requires novel approaches. Given the many contributors to our weight status, as well as the dynamic nature, genomic tools must be applied in an ecological model. Evaluating disparate factors can be difficult, such as feeding behavior, nutritional genomics, and gene-environment interaction. Many of these behaviors are being evaluated in animal models and hold great promise for targeted interventions in the future.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, et al. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994;372(6505):425–32. - PubMed
-
- Perusse L, Rankinen T, Zuberi A, et al. The human obesity gene map: The 2004 update. Obes Res. 2005;13(3):381–481. - PubMed
-
- Kirk S, Scott BJ, Daniels SR. Pediatric obesity epidemic: treatment options. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005;105(5 Suppl 1):S44–51. - PubMed
-
- Stewart L, Houghton J, Hughes AR, et al. Dietetic management of pediatric overweight: development and description of a practical and evidence-based behavioral approach. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005;105(11):1810–5. - PubMed
-
- Bautista-Castano I, Doreste J, Serra-Majem L. Effectiveness of interventions in the prevention of childhood obesity. Eur J Epidemiol. 2004;19(7):617–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

