Linking protein structure and dynamics to catalysis: the role of hydrogen tunnelling
- PMID: 16873120
- PMCID: PMC1647309
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2006.1870
Linking protein structure and dynamics to catalysis: the role of hydrogen tunnelling
Abstract
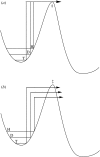
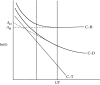
Early studies of enzyme-catalysed hydride transfer reactions indicated kinetic anomalies that were initially interpreted in the context of a 'tunnelling correction'. An alternate model for tunnelling emerged following studies of the hydrogen atom transfer catalysed by the enzyme soybean lipoxygenase. This invokes full tunnelling of all isotopes of hydrogen, with reaction barriers reflecting the heavy atom, environmental reorganization terms. Using the latter approach, we offer an integration of the aggregate data implicating hydrogen tunnelling in enzymes (i.e. deviations from Swain-Schaad relationships and the semi-classical temperature dependence of the hydrogen isotope effect). The impact of site-specific mutations of enzymes plays a critical role in our understanding of the factors that control tunnelling in enzyme reactions.
Figures



References
-
- Abad J.L, Camps F, Fabrias G. Is hydrogen tunneling involved in acyl-CoA desaturase reactions? The case of Δ9 desaturase that transforms (E)-11-tetradecenoic acid. Angew. Chem. (Intl. Ed.) 2000;39:3279–3281. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20000915)39:18<3279::AID-ANIE3279>3.0.CO;2-G - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bahnson B.J, Park D.H, Kim K, Plapp B.V, Klinman J.P. Unmasking of hydrogen tunneling in the horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase reaction by site directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1993;32:5503–5507. doi:10.1021/bi00072a003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bahnson B.J, Colby T.D, Chen J.K, Goldstein B.M, Klinman J.P. A link between protein structure and enzyme catalyzed hydrogen tunneling. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1997;94:12 797–12 802. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.24.12797 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basran J, Sutcliffe M.J, Scrutton N.S. Enzymatic H-transfer requires vibration-driven extreme tunneling. Biochemistry. 1999;38:3218–3222. doi:10.1021/bi982719d - DOI - PubMed
-
- Basran J, Sutcliffe M.J, Scrutton N.S. Deuterium isotope effects during carbon-hydrogen bond cleavage by trimethylamine dehydrogenase. Implications for mechanism and vibrationally assisted hydrogen tunneling in wild type and mutant enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:24 581–24 587. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101178200 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
