An analysis of reaction pathways for proton tunnelling in methylamine dehydrogenase
- PMID: 16873126
- PMCID: PMC1647307
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2006.1867
An analysis of reaction pathways for proton tunnelling in methylamine dehydrogenase
Abstract
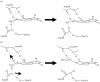
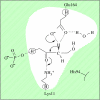
Computational methods have now become a valuable tool to understand the way in which enzymes catalyse chemical reactions and to aid the interpretation of a diverse set of experimental data. This study focuses on the influence of the condensed-phase environment structure on proton transfer mechanisms, with an aim to understand how C-H bond cleavage is mediated in enzymatic reactions. We shall use a combination of molecular simulation, ab initio or semi-empirical quantum chemistry and semi-classical multidimensional tunnelling methods to consider the primary kinetic isotope effects of the enzyme methylamine dehydrogenase (MADH), with reference to an analogous application to triosephosphate isomerase. Analysis of potentially reactive conformations of the system, and correlation with experimental isotope effects, have highlighted that a quantum tunnelling mechanism in MADH may be modulated by specific amino acid residues, such as Asp428, Thr474 and Asp384.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Analysis of classical and quantum paths for deprotonation of methylamine by methylamine dehydrogenase.Chemphyschem. 2007 Aug 24;8(12):1816-35. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200700143. Chemphyschem. 2007. PMID: 17676581
-
Direct dynamics calculations of reaction rate and kinetic isotope effects in enzyme catalysed reactions.Faraday Discuss. 2003;122:223-42; discussion 269-82. doi: 10.1039/b201183m. Faraday Discuss. 2003. PMID: 12555860 Review.
-
Computer simulations of quantum tunnelling in enzyme-catalysed hydrogen transfer reactions.Interdiscip Sci. 2010 Mar;2(1):78-97. doi: 10.1007/s12539-010-0093-y. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Interdiscip Sci. 2010. PMID: 20640799
-
Hydrogen tunnelling in enzyme-catalysed H-transfer reactions: flavoprotein and quinoprotein systems.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2006 Aug 29;361(1472):1375-86. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2006.1878. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16873125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Driving force analysis of proton tunnelling across a reactivity series for an enzyme-substrate complex.Chembiochem. 2008 Nov 24;9(17):2839-45. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200800408. Chembiochem. 2008. PMID: 19012287
Cited by
-
Promoting motions in enzyme catalysis probed by pressure studies of kinetic isotope effects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 9;104(2):507-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608408104. Epub 2007 Jan 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17202258 Free PMC article.
-
Does the pressure dependence of kinetic isotope effects report usefully on dynamics in enzyme H-transfer reactions?FEBS J. 2015 Aug;282(16):3243-55. doi: 10.1111/febs.13193. Epub 2015 Jan 29. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25581554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coupling Protein Dynamics with Proton Transport in Human Carbonic Anhydrase II.J Phys Chem B. 2016 Aug 25;120(33):8389-404. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b02166. Epub 2016 Apr 20. J Phys Chem B. 2016. PMID: 27063577 Free PMC article.
-
The enzyme aromatic amine dehydrogenase induces a substrate conformation crucial for promoting vibration that significantly reduces the effective potential energy barrier to proton transfer.J R Soc Interface. 2008 Dec 6;5 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S225-32. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0068.focus. J R Soc Interface. 2008. PMID: 18495615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aaqvist J, Fothergill M. Computer simulation of the triosephosphate isomerase catalyzed reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:10 010–10 016. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.17.10010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alagona G, Ghio C, Kollman P.A. Do enzymes stabilize transition states by electrostatic interactions or pKa balance: the case of triosephosphate isomerase (TIM)? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995;117:9855–9862. doi:10.1021/ja00144a011 - DOI
-
- Albery W.J, Knowles J.R. Deuterium and tritium exchange in enzyme kinetics. Biochemistry. 1976;15:5588–5600. doi:10.1021/bi00670a025 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alhambra C, Gao J, Corchado J.C, Villa J, Truhlar D.G. Quantum mechanical dynamical effects in an enzyme-catalyzed proton transfer reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:2253–2258. doi:10.1021/ja9831655 - DOI
-
- Alhambra C, Sanchez M.L, Corchado J.C, Gao J, Truhlar D.G. Erratum to: “Quantum mechanical tunneling in methylamine dehydrogenase” [Chem. Phys. Lett. 347 (2001) 512–518] Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002;355:388–394. doi:10.1016/S0009-2614(02)00057-X - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

