Differential role of Sp100 isoforms in interferon-mediated repression of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein expression
- PMID: 16873258
- PMCID: PMC1563809
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02164-05
Differential role of Sp100 isoforms in interferon-mediated repression of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein expression
Abstract
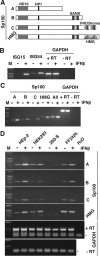
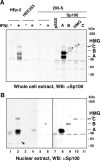
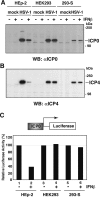
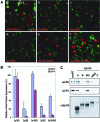
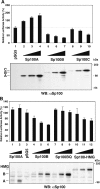
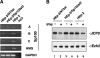
Nuclear domains called ND10 or PML nuclear bodies contain interferon (IFN)-upregulated proteins like PML and Sp100. Paradoxically, herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) begins its transcriptional cascade at aggregates of ND10-associated proteins, which in turn are destroyed by the HSV-1 immediate-early protein ICP0. While PML is essential in the formation of ND10, the function of Sp100 in the cells' defense against viral infection is unknown. In this study we investigated the potential antiviral effect of IFN-beta-induced Sp100. We found that IFN-beta treatment leads to a differential accumulation of four Sp100 isoforms in different cell lines. Using an HEK293 cell line derivative, 293-S, producing no detectable amounts of Sp100 even after IFN exposure, we analyzed individual Sp100 isoforms for their effect on HSV-1 infection. Sp100 isoforms B, C, and HMG, but not Sp100A, suppressed ICP0 and ICP4 early after infection. Isoforms B, C, and HMG suppressed expression from the ICP0 promoter in transient transfection, whereas Sp100A enhanced expression. Moreover, Sp100A localized in ND10, whereas the repressive isoforms were either dispersed within the nucleus or, at unphysiologically higher expression levels, formed new aggregates. The repressive activity was dependent on an intact SAND domain, since Sp100B bearing a W655Q mutation in the SAND domain lost this repressive activity and accumulated in ND10. Using RNA interference to knock down the repressive Sp100 isoforms B, C, and HMG, we find that they are an essential part of the IFN-beta-mediated suppression of ICP0 expression. These data suggest that repression by the Sp100 isoforms B, C, and HMG takes place outside of ND10 and raise the possibility that viral genomes at Sp100A accumulations are more likely to start their transcription program because of a more permissive local environment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential functions of interferon-upregulated Sp100 isoforms: herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter-based immediate-early gene suppression and PML protection from ICP0-mediated degradation.J Virol. 2009 May;83(10):5168-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02083-08. Epub 2009 Mar 11. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19279115 Free PMC article.
-
PML plays both inimical and beneficial roles in HSV-1 replication.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 May 24;113(21):E3022-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1605513113. Epub 2016 May 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27162364 Free PMC article.
-
Two overlapping regions within the N-terminal half of the herpes simplex virus 1 E3 ubiquitin ligase ICP0 facilitate the degradation and dissociation of PML and dissociation of Sp100 from ND10.J Virol. 2013 Dec;87(24):13287-96. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02304-13. Epub 2013 Oct 2. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 24089549 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of alphaherpesvirus infections by the ICP0 family of proteins.J Gen Virol. 2013 Mar;94(Pt 3):465-481. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.048900-0. Epub 2012 Dec 12. J Gen Virol. 2013. PMID: 23239572 Review.
-
Role of ND10 nuclear bodies in the chromatin repression of HSV-1.Virol J. 2016 Apr 5;13:62. doi: 10.1186/s12985-016-0516-4. Virol J. 2016. PMID: 27048561 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multifaceted Histone H3 Methylation and Phosphorylation Readout by the Plant Homeodomain Finger of Human Nuclear Antigen Sp100C.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 10;291(24):12786-12798. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.721159. Epub 2016 Apr 22. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27129259 Free PMC article.
-
Sp100 provides intrinsic immunity against human papillomavirus infection.mBio. 2013 Nov 5;4(6):e00845-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00845-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 24194542 Free PMC article.
-
A Tale of Usurpation and Subversion: SUMO-Dependent Integrity of Promyelocytic Leukemia Nuclear Bodies at the Crossroad of Infection and Immunity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 27;9:696234. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.696234. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34513832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon Kappa Inhibits Human Papillomavirus 31 Transcription by Inducing Sp100 Proteins.J Virol. 2015 Oct 21;90(2):694-704. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02137-15. Print 2016 Jan 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26491169 Free PMC article.
-
Host cell restriction factors that limit transcription and replication of human papillomavirus.Virus Res. 2017 Mar 2;231:10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.11.014. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27863967 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bloch, D. B., S. M. de la Monte, P. Guigaouri, A. Filippov, and K. D. Bloch. 1996. Identification and characterization of a leukocyte-specific component of the nuclear body. J. Biol. Chem. 271:29198-29204. - PubMed
-
- Boddy, M. N., K. Howe, L. D. Etkin, E. Solomon, and P. S. Freemont. 1996. PIC 1, a novel ubiquitin-like protein which interacts with the PML component of a multiprotein complex that is disrupted in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Oncogene 13:971-982. - PubMed
-
- Bottomley, M. J., M. W. Collard, J. I. Huggenvik, Z. Liu, T. J. Gibson, and M. Sattler. 2001. The SAND domain structure defines a novel DNA-binding fold in transcriptional regulation. Nat. Struct. Biol. 8:626-633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

