Virion-associated restriction endonucleases of chloroviruses
- PMID: 16873267
- PMCID: PMC1563800
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00486-06
Virion-associated restriction endonucleases of chloroviruses
Abstract
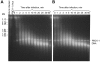
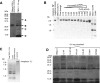
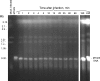
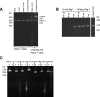
Chloroviruses are large, double-stranded-DNA, plaque-forming viruses that infect certain eukaryotic chlorella-like green algae. The prototype of the genus is Paramecium bursaria chlorella virus 1 (PBCV-1). Chlorovirus genomes contain various amounts of methylated nucleotides due to virus-encoded DNA methyltransferases (MTases); about 25% of the MTases are associated with companion DNA site-specific (restriction) endonucleases (REases). These enzymes constitute virally encoded restriction-modification (R/M) systems. Although several of the chlorovirus R/M systems are characterized, their biological functions are unknown. The PBCV-1 proteome reveals that two virus-encoded REases, but not their companion MTases, are virion associated, suggesting that viral REases might help degrade the host DNA early in infection. To test this hypothesis, host chromosomal DNA from PBCV-1-infected cells was examined by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Initiation of host chromosomal DNA degradation occurred within 5 min postinfection (p.i.). The DNA degradation was insensitive to protein synthesis inhibitors or UV inactivation of virus particles, consistent with the agent being a small protein associated with the virion. Nuclease activities, including those of the two predicted REases and an uncharacterized general nuclease(s), were detected in disrupted PBCV-1 particles. The general nuclease(s) degraded both host and viral DNAs in vitro, although the viral DNA was not degraded in vivo, suggesting differential intracellular trafficking of the virion-associated nucleases. Infection with chloroviruses lacking an R/M system(s) resulted in either delayed host chromosomal DNA degradation or no detectable host chromatin changes. These immediate-early events associated with chlorovirus infections may facilitate rapid switching of the host transcriptional apparatus to viral transcription, which begins within 5 to 10 min p.i.
Figures

References
-
- Birren, B., and E. Lai. 1993. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis. A practical guide. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, Calif.
-
- Blank, A., R. H. Sugiyama, and C. A. Dekker. 1982. Activity staining of nucleolytic enzymes after dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: use of aqueous isopropanol to remove detergent from gels. Anal. Biochem. 120:267-275. - PubMed
-
- Burbank, D. E., S. L. Shields, A. M. Schuster, and J. L. Van Etten. 1990. 5-Azacytidine resistant mutants of Chlorella virus IL-3A. Virology 176:311-315. - PubMed
-
- Chan, S.-H., Z. Zhu, D. D. Dunigan, J. L. Van Etten, and S.-Y. Xu. 2006. Cloning of Nt.CviQII nicking endonuclease and its cognate methyltransferase: M.CviQII methylates AG sequences. Protein Expr. Purif. [Epub ahead of print.] - PubMed
-
- Chase, T. E., J. A. Nelson, D. E. Burbank, and J. L. Van Etten. 1989. Mutual exclusion occurs in a chlorella-like green alga inoculated with two viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 70:1829-1836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

