Nitric oxide-induced mitochondrial fission is regulated by dynamin-related GTPases in neurons
- PMID: 16874299
- PMCID: PMC1553198
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601253
Nitric oxide-induced mitochondrial fission is regulated by dynamin-related GTPases in neurons
Abstract
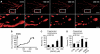
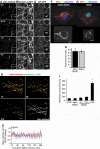
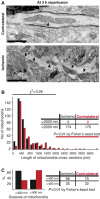
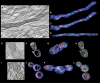
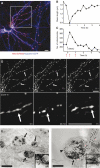
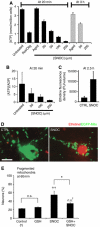
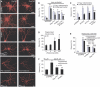
Mitochondria are present as tubular organelles in neuronal projections. Here, we report that mitochondria undergo profound fission in response to nitric oxide (NO) in cortical neurons of primary cultures. Mitochondrial fission by NO occurs long before neurite injury and neuronal cell death. Furthermore, fission is accompanied by ultrastructural damage of mitochondria, autophagy, ATP decline and generation of free radicals. Fission is occasionally asymmetric and can be reversible. Strikingly, mitochondrial fission is also an early event in ischemic stroke in vivo. Mitofusin 1 (Mfn1) or dominant-negative Dynamin related protein 1 (Drp1(K38A)) inhibits mitochondrial fission induced by NO, rotenone and Amyloid-beta peptide. Conversely, overexpression of Drp1 or Fis1 elicits fission and increases neuronal loss. Importantly, NO-induced neuronal cell death was mitigated by Mfn1 and Drp1(K38A). Thus, persistent mitochondrial fission may play a causal role in NO-mediated neurotoxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Beal MF (2000) Energetics in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci 23: 298–304 - PubMed
-
- Bereiter-Hahn J, Voth M (1994) Dynamics of mitochondria in living cells: shape changes, dislocations, fusion, and fission of mitochondria. Microsc Res Tech 27: 198–219 - PubMed
-
- Betarbet R, Sherer TB, MacKenzie G, Garcia-Osuna M, Panov AV, Greenamyre JT (2000) Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson's disease. Nat Neurosci 3: 1301–1306 - PubMed
-
- Boje KM (2004) Nitric oxide neurotoxicity in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Biosci 9: 763–776 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS044326/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY009024/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS044314/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P41RR04050/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY016164/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS14718/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY005477/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS43242/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR004050/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY05477/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS014718/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY09024/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS44314/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI055789/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD029587/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047973/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS043242/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047456/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS046994/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047456-S3/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD29587/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

