The imprinted Air ncRNA is an atypical RNAPII transcript that evades splicing and escapes nuclear export
- PMID: 16874305
- PMCID: PMC1538572
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601245
The imprinted Air ncRNA is an atypical RNAPII transcript that evades splicing and escapes nuclear export
Abstract
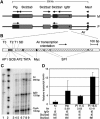
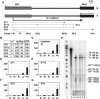
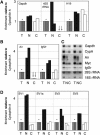
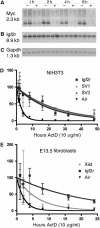
Expression of the Air ncRNA is necessary to silence multiple genes in cis in the imprinted Igf2r cluster. However, its mode of action is unknown. Here, we characterize co- and post-transcriptional features of Air that identify it as a new member of the class of nuclear regulatory RNAs. We show that Air is transcribed from a DNA methylation-sensitive promoter by RNA polymerase II (RNAPII). However, although it is capped and polyadenylated similar to other RNAPII transcripts, the majority of Air transcripts evade cotranscriptional splicing resulting in a mature 108 kb ncRNA. As a consequence, the mature unspliced Air is nuclear localized and highly unstable. These features show that Air is an atypical RNAPII transcript whose properties indicate that its mode of action in gene silencing may not depend on the RNA per se but instead is related to its actual transcription.
Figures




References
-
- Chamberlain SJ, Brannan CI (2001) The Prader–Willi syndrome imprinting center activates the paternally expressed murine Ube3a antisense transcript but represses paternal Ube3a. Genomics 73: 316–322 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

