Yeast homolog of a cancer-testis antigen defines a new transcription complex
- PMID: 16874308
- PMCID: PMC1538566
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601235
Yeast homolog of a cancer-testis antigen defines a new transcription complex
Abstract
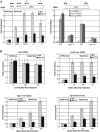
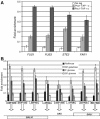
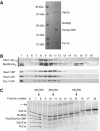
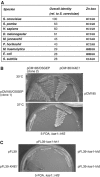
We have isolated a new yeast gene (PCC1) that codes for a factor homologous to human cancer-testis antigens. We provide evidence that Pcc1p is a new transcription factor and that its mutation affects expression of several genes, some of which are involved in cell cycle progression and polarized growth. Mutation of Pcc1p also affects the expression of GAL genes by impairing the recruitment of the SAGA and Mediator co-activators. We characterize a new complex that contains Pcc1p, a kinase, Bud32p, a putative endopeptidase, Kae1p and two additional proteins encoded by ORFs YJL184w and YMLO36w. Genetic and physical interactions among these proteins strongly suggest that this complex is a functional unit. Chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments and multiple genetic interactions of pcc1 mutants with mutants of the transcription apparatus and chromatin modifying enzymes underscore the direct role of the complex in transcription. Functional complementation experiments indicate that the transcriptional function of this set of genes is conserved throughout evolution.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous recruitment of coactivators by Gcn4p stimulates multiple steps of transcription in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;25(13):5626-38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.13.5626-5638.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15964818 Free PMC article.
-
A study of biochemical and functional interactions of Htl1p, a putative component of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Rsc chromatin-remodeling complex.Gene. 2007 Jun 15;395(1-2):72-85. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2007.02.002. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17400406
-
Phosphorylation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Grx4p glutaredoxin by the Bud32p kinase unveils a novel signaling pathway involving Sch9p, a yeast member of the Akt / PKB subfamily.FEBS J. 2008 Dec;275(23):5919-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06721.x. FEBS J. 2008. PMID: 19021767
-
Mediator complexes and eukaryotic transcription regulation: an overview.Biochimie. 2007 Dec;89(12):1439-46. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2007.08.002. Epub 2007 Aug 11. Biochimie. 2007. PMID: 17870225 Review.
-
[Mediator complexes in gene transcription].Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2003 Oct;34(4):298-302. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2003. PMID: 14992009 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis delay a family of Galloway-Mowat Syndrome caused by a classical splicing mutation of Lage3.BMC Nephrol. 2023 Feb 8;24(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-03000-5. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36755238 Free PMC article.
-
The highly conserved KEOPS/EKC complex is essential for a universal tRNA modification, t6A.EMBO J. 2011 Mar 2;30(5):873-81. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.343. Epub 2010 Dec 24. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21183954 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal domain of the novel essential protein Gcp is critical for interaction with another essential protein YeaZ of Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20163. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020163. Epub 2011 May 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21625506 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for t6A modification in human mitochondria.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Apr 6;48(6):3181-3194. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa093. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32047918 Free PMC article.
-
Kinase-associated endopeptidase 1 (Kae1) participates in an atypical ribosome-associated complex in the apicoplast of Plasmodium falciparum.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 24;289(43):30025-39. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.586735. Epub 2014 Sep 9. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25204654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe Y, Matsumoto S, Wei S, Nezu K, Miyoshi A, Kito K, Ueda N, Shigemoto K, Hitsumoto Y, Nikawa J, Enomoto Y (2001) Cloning and characterization of a p53-related protein kinase expressed in interleukin-2-activated cytotoxic T-cells, epithelial tumor cell lines, and the testes. J Biol Chem 276: 44003–44011 - PubMed
-
- Alpen B, Gure AO, Scanlan MJ, Old LJ, Chen YT (2002) A new member of the NY-ESO-1 gene family is ubiquitously expressed in somatic tissues and evolutionarily conserved. Gene 297: 141–149 - PubMed
-
- Aravind L, Koonin EV (1999) Gleaning non-trivial structural, functional and evolutionary information about proteins by iterative database searches. J Mol Biol 287: 1023–1040 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

