Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): chemical and biomedical perspectives
- PMID: 16876833
- PMCID: PMC2903211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.06.020
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): chemical and biomedical perspectives
Abstract
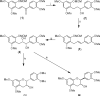
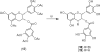
The compound (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is the major catechin found in green tea [Camellia sinensis L. Ktze. (Theaceae)]. This polyphenolic compound and several related catechins are believed to be responsible for the health benefits associated with the consumption of green tea. The potential health benefits ascribed to green tea and EGCG include antioxidant effects, cancer chemoprevention, improving cardiovascular health, enhancing weight loss, protecting the skin from the damage caused by ionizing radiation, and others. The compound EGCG has been shown to regulate dozens of disease-specific molecular targets. Many of these molecular targets are only affected by concentrations of EGCG that are far above the levels achieved by either drinking green tea or consuming moderate doses of green tea extract-based dietary supplements. In spite of this, well-designed double-blinded controlled clinical studies have recently demonstrated the efficacy of green tea extracts and purified EGCG products in patients. Therefore, this review highlights results from what the authors believe to be some of the most clinically significant recent studies and describes current developments in the stereoselective total synthesis of EGCG.
Figures

References
-
- Abe I, Seki T, Umehara K, Miyase T, Noguchi H, Sakakibara J, Ono T. Green tea polyphenols: novel and potent inhibitors of squalene epoxidase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000;268:767–771. - PubMed
-
- Adhami VM, Ahmad N, Mukhtar H. Molecular targets for green tea in prostate cancer prevention. J. Nutr. 2003;133(Suppl.):2417S–2424S. - PubMed
-
- Ahn W-S, Huh SW, Bae S-M, Lee I-P, Lee J-M, Namkoong S-E, Kim C-K, Sin J-I. A major constituent of green tea, EGCG, inhibits the growth of a human cervical cancer cell line, CaSki cells, through apoptosis, G(1) arrest, and regulation of gene expression. DNA Cell Biol. 2003a;22:217–224. - PubMed
-
- Ahn W-S, Yoo J, Huh SW, Kim C-K, Lee J-M, Namkoong S-E, Bae S-M, Lee IP. Protective effects of green tea extracts (polyphenon E and EGCG) on human cervical lesions. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2003b;12:383–390. - PubMed
-
- Bettuzzi S, Brausi M, Rizzi F, Castagnetti G, Peracchia G, Corti A. Chemoprevention of human prostate cancer by oral administration of green tea catechins in volunteers with high-grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia: a preliminary report from a one-year proof-of-principle study. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1234–1240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

