A tyrosine hydroxylase-yellow fluorescent protein knock-in reporter system labeling dopaminergic neurons reveals potential regulatory role for the first intron of the rodent tyrosine hydroxylase gene
- PMID: 16876957
- PMCID: PMC2610443
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.06.032
A tyrosine hydroxylase-yellow fluorescent protein knock-in reporter system labeling dopaminergic neurons reveals potential regulatory role for the first intron of the rodent tyrosine hydroxylase gene
Abstract
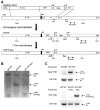
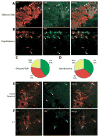
Degeneration of the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra is a hallmark of Parkinson's disease. To facilitate the study of the differentiation and maintenance of this population of dopaminergic neurons both in vivo and in vitro, we generated a knock-in reporter line in which the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) replaced the first exon and the first intron of the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) gene in one allele by homologous recombination. Expression of YFP under the direct control of the entire endogenous 5' upstream region of the TH gene was predicted to closely match expression of TH from the wild type allele, thus marking functional dopaminergic neurons. We found that YFP was expressed in dopaminergic neurons differentiated in vitro from the knock-in mouse embryonic stem cell line and in dopaminergic brain regions in knock-in mice. Surprisingly, however, YFP expression did not overlap completely with TH expression, and the degree of overlap varied in different TH-expressing brain regions. Thus, the reporter gene did not identify functional TH-expressing cells with complete accuracy. A DNaseI hypersensitivity assay revealed a cluster of hypersensitivity sites in the first intron of the TH gene, which was deleted by insertion of the reporter gene, suggesting that this region may contain cis-acting regulatory sequences. Our results suggest that the first intron of the rodent TH gene may be important for accurate expression of TH.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pitx3 regulates tyrosine hydroxylase expression in the substantia nigra and identifies a subgroup of mesencephalic dopaminergic progenitor neurons during mouse development.Dev Biol. 2005 Jun 15;282(2):467-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.03.028. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 15950611
-
Cloning and cell type-specific regulation of the human tyrosine hydroxylase gene promoter.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Dec 26;312(4):1123-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.029. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. PMID: 14651989
-
Rat tyrosine hydroxylase promoter directs tetracycline-inducible foreign gene expression in dopaminergic cell types.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004 Jul 26;126(2):173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.04.008. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15249141
-
Analysis of dopaminergic neuron-specific mitochondrial morphology and function using tyrosine hydroxylase reporter iPSC lines.Anat Sci Int. 2025 Mar;100(2):155-162. doi: 10.1007/s12565-024-00816-z. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Anat Sci Int. 2025. PMID: 39612053 Review.
-
Moving beyond tyrosine hydroxylase to define dopaminergic neurons for use in cell replacement therapies for Parkinson's disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012 Jun 1;11(4):340-9. doi: 10.2174/187152712800792758. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22483315 Review.
Cited by
-
Complex molecular regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014 Dec;121(12):1451-81. doi: 10.1007/s00702-014-1238-7. Epub 2014 May 28. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014. PMID: 24866693 Review.
-
Preserved dopaminergic homeostasis and dopamine-related behaviour in hemizygous TH-Cre mice.Eur J Neurosci. 2017 Jan;45(1):121-128. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13347. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Eur J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27453291 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation of nuclear fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 and Nurr1 offers new interactive mechanism in postmitotic development of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 8;287(24):19827-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.347831. Epub 2012 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22514272 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription and epigenetic profile of the promoter, first exon and first intron of the human tyrosine hydroxylase gene.J Cell Physiol. 2007 May;211(2):431-8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20949. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17195153 Free PMC article.
-
A novel dopamine transporter transgenic mouse line for identification and purification of midbrain dopaminergic neurons reveals midbrain heterogeneity.Eur J Neurosci. 2015 Oct;42(7):2438-54. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13046. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Eur J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26286107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albanese V, Biguet NF, Kiefer H, Bayard E, Mallet J, Meloni R. Quantitative effects on gene silencing by allelic variation at a tetranucleotide microsatellite. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:1785–1792. - PubMed
-
- Andersson E, Tryggvason U, Deng Q, Friling S, Alekseenko Z, Robert B, Perlmann T, Ericson J. Identification of intrinsic determinants of midbrain dopamine neurons. Cell. 2006;124:393–405. - PubMed
-
- Barberi T, Klivenyi P, Calingasan NY, Lee H, Kawamata H, Loonam K, Perrier AL, Bruses J, Rubio ME, Topf N, Tabar V, Harrison NL, Beal MF, Moore MA, Studer L. Neural subtype specification of fertilization and nuclear transfer embryonic stem cells and application in parkinsonian mice. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:1200–1207. - PubMed
-
- Best JA, Chen Y, Piech KM, Tank AW. The response of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene to cyclic AMP is mediated by two cyclic AMP-response elements. J Neurochem. 1995;65:1934–1943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

