The molecular biology of coronaviruses
- PMID: 16877062
- PMCID: PMC7112330
- DOI: 10.1016/S0065-3527(06)66005-3
The molecular biology of coronaviruses
Abstract
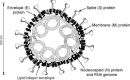
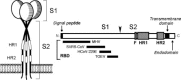
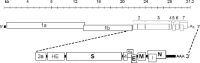
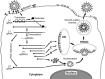
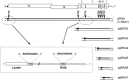
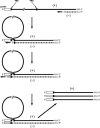
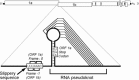
Coronaviruses are large, enveloped RNA viruses of both medical and veterinary importance. Interest in this viral family has intensified in the past few years as a result of the identification of a newly emerged coronavirus as the causative agent of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). At the molecular level, coronaviruses employ a variety of unusual strategies to accomplish a complex program of gene expression. Coronavirus replication entails ribosome frameshifting during genome translation, the synthesis of both genomic and multiple subgenomic RNA species, and the assembly of progeny virions by a pathway that is unique among enveloped RNA viruses. Progress in the investigation of these processes has been enhanced by the development of reverse genetic systems, an advance that was heretofore obstructed by the enormous size of the coronavirus genome. This review summarizes both classical and contemporary discoveries in the study of the molecular biology of these infectious agents, with particular emphasis on the nature and recognition of viral receptors, viral RNA synthesis, and the molecular interactions governing virion assembly.
Figures

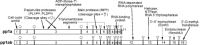
References
-
- Almeida J.D., Tyrrell D.A. The morphology of three previously uncharacterized human respiratory viruses that grow in organ culture. J. Gen. Virol. 1967;1:175–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

