Distribution, structure and diversity of "bacterial" genes encoding two-component proteins in the Euryarchaeota
- PMID: 16877318
- PMCID: PMC2685588
- DOI: 10.1155/2006/562404
Distribution, structure and diversity of "bacterial" genes encoding two-component proteins in the Euryarchaeota
Abstract
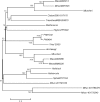
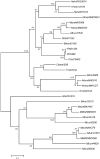
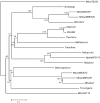
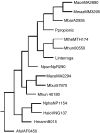
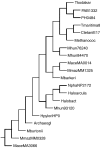
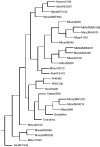
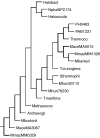
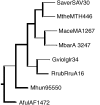
The publicly available annotated archaeal genome sequences (23 complete and three partial annotations, October 2005) were searched for the presence of potential two-component open reading frames (ORFs) using gene category lists and BLASTP. A total of 489 potential two-component genes were identified from the gene category lists and BLASTP. Two-component genes were found in 14 of the 21 Euryarchaeal sequences (October 2005) and in neither the Crenarchaeota nor the Nanoarchaeota. A total of 20 predicted protein domains were identified in the putative two-component ORFs that, in addition to the histidine kinase and receiver domains, also includes sensor and signalling domains. The detailed structure of these putative proteins is shown, as is the distribution of each class of two-component genes in each species. Potential members of orthologous groups have been identified, as have any potential operons containing two or more two-component genes. The number of two-component genes in those Euryarchaeal species which have them seems to be linked more to lifestyle and habitat than to genome complexity, with most examples being found in Methanospirillum hungatei, Haloarcula marismortui, Methanococcoides burtonii and the mesophilic Methanosarcinales group. The large numbers of two-component genes in these species may reflect a greater requirement for internal regulation. Phylogenetic analysis of orthologous groups of five different protein classes, three probably involved in regulating taxis, suggests that most of these ORFs have been inherited vertically from an ancestral Euryarchaeal species and point to a limited number of key horizontal gene transfer events.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nanoarchaea: representatives of a novel archaeal phylum or a fast-evolving euryarchaeal lineage related to Thermococcales?Genome Biol. 2005;6(5):R42. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-5-r42. Epub 2005 Apr 14. Genome Biol. 2005. PMID: 15892870 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics of the Archaea (Euryarchaeota): evolution of conserved protein families, the stable core, and the variable shell.Genome Res. 1999 Jul;9(7):608-28. Genome Res. 1999. PMID: 10413400
-
Complete genome sequence of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum deltaH: functional analysis and comparative genomics.J Bacteriol. 1997 Nov;179(22):7135-55. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.22.7135-7155.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9371463 Free PMC article.
-
Novel domains of the prokaryotic two-component signal transduction systems.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001 Sep 11;203(1):11-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10814.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11557134 Review.
-
Two-component systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: why so many?Trends Microbiol. 2000 Nov;8(11):498-504. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(00)01833-3. Trends Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11121759 Review.
Cited by
-
The Journey from Two-Step to Multi-Step Phosphorelay Signaling Systems.Curr Genomics. 2021 Jan;22(1):59-74. doi: 10.2174/1389202921666210105154808. Curr Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34045924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution and phyletic distribution of two-component signal transduction systems.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010 Apr;13(2):219-25. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2009.12.011. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20133179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of an archaeal two-component system that regulates methanogenesis in Methanosaeta harundinacea.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 18;9(4):e95502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095502. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24748383 Free PMC article.
-
The mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes of the haptophyte Chrysochromulina tobin contain unique repeat structures and gene profiles.BMC Genomics. 2014 Jul 17;15:604. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-604. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25034814 Free PMC article.
-
Phyletic Distribution and Lineage-Specific Domain Architectures of Archaeal Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems.J Bacteriol. 2018 Mar 12;200(7):e00681-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00681-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29263101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alves R., Savageau M.A. Comparative analysis of prototype two-component systems with either bifunctional or monofunctional sensors: differences in molecular structure and physiological function. Mol. Microbiol. 2003;48:25–51. - PubMed
-
- Anantharaman V., Aravind L. The CHASE domain: a predicted ligand-binding module in plant cytokinin receptors and other eukaryotic and bacterial receptors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001;26:579–582. - PubMed
-
- Anantharaman V., Koonin E.V., Aravind L. Regulatory potential, phyletic distribution and evolution of ancient, intracelluar small-molecule-binding domains. J. Mol. Biol. 2001;307:1271–1292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

