MDM2: a novel mineralocorticoid-responsive gene involved in aldosterone-induced human vascular structural remodeling
- PMID: 16877339
- PMCID: PMC1698800
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.051351
MDM2: a novel mineralocorticoid-responsive gene involved in aldosterone-induced human vascular structural remodeling
Abstract
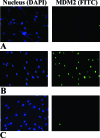
Aldosterone has been demonstrated to play an important role in the pathogenesis of various cardiovascular diseases. Vascular structural remodeling, including vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation, has been also reported in small resistance arteries of patients with primary aldosteronism. Therefore, in this study, we examined whether genes involved in the regulation of the cell cycle were induced by aldosterone alone in cultured human VSMCs and in human small resistance arteries. Results of these studies eventually demonstrated that MDM2, one of the genes involved in anti-apoptosis and cell growth, was markedly increased in mineralocorticoid receptor (MR)-positive VSMCs by aldosterone in all microarray, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, immunoblotting, and immunofluorescence analyses. In addition, an analysis using small interfering RNA demonstrated that this gene product was involved in cell proliferation of VSMCs induced by aldosterone. Eplerenone, a specific MR antagonist, inhibited this gene induction by aldosterone in VSMCs. MDM2 protein was also more abundant in VSMCs of small resistance arteries in patients with primary aldosteronism compared with a control population. MDM2 is therefore considered one of the mineralocorticoid-responsive genes that regulates cell proliferation of VSMCs induced by MR-mediated aldosterone stimulation, possibly playing an important role in aldosterone-induced vascular structural remodeling.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II and aldosterone regulate gene transcription via functional mineralocortocoid receptors in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells.Circ Res. 2005 Apr 1;96(6):643-50. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000159937.05502.d1. Epub 2005 Feb 17. Circ Res. 2005. PMID: 15718497
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism protects the aorta from vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and collagen deposition in a rat model of adrenal aldosterone-producing adenoma.J Physiol Biochem. 2018 Feb;74(1):17-24. doi: 10.1007/s13105-017-0600-2. Epub 2017 Nov 21. J Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29164516
-
Activated mineralocorticoid receptor regulates micro-RNA-29b in vascular smooth muscle cells.FASEB J. 2016 Apr;30(4):1610-22. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-271254. Epub 2016 Jan 4. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26728178
-
Mineralocorticoid action.Steroids. 2000 Feb;65(2):61-73. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(99)00087-2. Steroids. 2000. PMID: 10639017 Review.
-
[Agonists and antagonists of mineralocorticoids. The relation between structure and activity].Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2004 Jun;53(3):154-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ancard.2004.02.018. Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2004. PMID: 15291173 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Vasohibin-1 as a potential predictor of aggressive behavior of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast.Cancer Sci. 2010 Apr;101(4):1051-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01483.x. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20704578 Free PMC article.
-
The mineralocorticoid receptor: insights into its molecular and (patho)physiological biology.Nucl Recept Signal. 2007 Nov 30;5:e012. doi: 10.1621/nrs.05012. Nucl Recept Signal. 2007. PMID: 18174920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of lung p53 by Nutlin-3a prevents and reverses experimental pulmonary hypertension.Circulation. 2013 Apr 23;127(16):1664-76. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.002434. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Circulation. 2013. PMID: 23513067 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-related receptor α in normal adrenal cortex and adrenocortical tumors: involvement in development and oncogenesis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Jan 30;365(2):207-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.10.020. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23123734 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension: lessons from cancer.Eur Respir Rev. 2013 Dec;22(130):543-51. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00007513. Eur Respir Rev. 2013. PMID: 24293470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jaffe IZ, Mendelsohn ME. Angiotensin II and aldosterone regulate gene transcription via functional mineralocortocoid receptors in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 2005;96:643–650. - PubMed
-
- Tsai MJ, O’Malley BW. Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:451–486. - PubMed
-
- Pitt B, Remme W, Zannad F, Neaton J, Martinez F, Roniker B, Bittman R, Hurley S, Kleiman J, Gatlin M. Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1309–1321. - PubMed
-
- Xiao F, Puddefoot JR, Barker S, Vinson GP. Mechanism for aldosterone potentiation of angiotensin II-stimulated rat arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation. Hypertension. 2004;44:340–345. - PubMed
-
- Min LJ, Mogi M, Li JM, Iwanami J, Iwai M, Horiuchi M. Aldosterone and angiotensin II synergistically induce mitogenic response in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 2005;97:434–442. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

