Mechanotransduction of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in smooth muscle is dependent on the extracellular matrix and regulated by matrix metalloproteinases
- PMID: 16877348
- PMCID: PMC1698787
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050969
Mechanotransduction of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in smooth muscle is dependent on the extracellular matrix and regulated by matrix metalloproteinases
Abstract
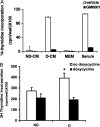
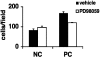
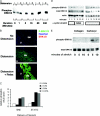
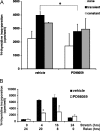
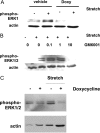
Excessive wall stretch of distensible hollow organs in cardiovascular and urinary systems can activate matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), thereby releasing matrix neoepitopes and growth factor ligands, leading to ERK1/2 activation. However, the role of MMPs in mechanotransduction of ERK1/2 signaling in the bladder is unknown. We examined bladders undergoing sustained distension over time, which provides a novel platform for smooth muscle mechanotransduction studies. Bladder distension ex vivo caused increased proliferation and MMP activity. Conditioned medium from distended compared with undistended bladders induced proliferation in bladder smooth muscle cells (BSMCs). When conditioned medium from distended bladders was used to proteolyze collagen type I matrices, matrices augmented BSMC proliferation, which was inhibited if bladders were distended in presence of broad-spectrum MMP inhibitors. Distension of ex vivo bladders also induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation in situ, which was dependent on MMP activity in the intact bladder. Similarly, stretching BSMCs in vitro induced increases in ERK1/2 activation and ERK1/2-dependent proliferation under discrete mechanical conditions, and distension conditioned medium itself induced MMP-dependent ERK1/2 activation in BSMCs. Overall, stretch-induced proliferation and ERK1/2 signaling in bladder tissue and BSMCs likely depend on secreted MMP activity. Identification of intermediaries between MMPs and ERK1/2 may elaborate novel mechanisms underlying mechanotransduction in bladder smooth muscle.
Figures



References
-
- Capolicchio G, Aitken KJ, Gu JX, Reddy P, Bagli DJ. Extracellular matrix gene responses in a novel ex vivo model of bladder stretch injury. J Urol. 2001;165:2235–2240. - PubMed
-
- Levin R, Levin S, Zhao Y, Buttyan R. Cellular and molecular aspects of bladder hypertrophy. Eur Urol. 1997;32(Suppl 1):15–21. - PubMed
-
- Polyakova V, Hein S, Kostin S, Ziegelhoeffer T, Schaper J. Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in pressure-overloaded human myocardium during heart failure progression. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:1609–1618. - PubMed
-
- Iwanaga Y, Aoyama T, Kihara Y, Onozawa Y, Yoneda T, Sasayama S. Excessive activation of matrix metalloproteinases coincides with left ventricular remodeling during transition from hypertrophy to heart failure in hypertensive rats. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39:1384–1391. - PubMed
-
- Sutherland RS, Baskin LS, Elfman F, Hayward SW, Cunha GR. The role of type IV collagenases in rat bladder development and obstruction. Pediatr Res. 1997;41:430–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

