STAT-6-mediated control of P-selectin by substance P and interleukin-4 in human dermal endothelial cells
- PMID: 16877367
- PMCID: PMC1698799
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.051211
STAT-6-mediated control of P-selectin by substance P and interleukin-4 in human dermal endothelial cells
Abstract
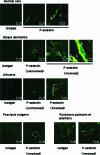
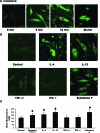
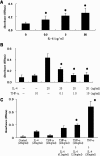
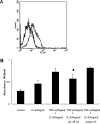
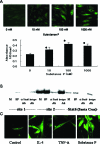
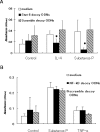
P-Selectin expressed on endothelial cells contributes to acute and chronic inflammation by promoting leukocyte tethering/rolling. Despite increasing evidence of P-selectin expression on human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro, the regulatory mechanisms of P-selectin expression on dermal endothelial cells in skin diseases are not fully understood. Here, we demonstrate increased expression of P-selectin in dermal vessels of regional skin in urticaria and atopic dermatitis. The present in vitro analyses with human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMECs) revealed that histamine rapidly induced P-selectin expression. Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 induced prolonged expression of surface P-selectin by HDMECs. A combination of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-4 inhibited P-selectin expression. Pretreatment of HDMECs with tumor necrosis factor-alpha followed by incubation with IL-4 markedly increased P-selectin expression. Notably, incubation with substance P alone induced prolonged P-selectin expression. Activation of STAT6 appears to be a key factor in P-selectin expression induced by substance P and IL-4 because treatment with STAT6 decoy oligodeoxynucleotides significantly inhibited P-selectin expression. The present results indicate that novel, complex mechanisms are involved in endothelial P-selectin expression in the skin. STAT6 in dermal endothelial cells appears to be a potent target for controlling cellular infiltrate in allergic and/or neuroinflammatory skin diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Catalina MD, Estess P, Siegelman MH. Selective requirements for leukocyte adhesion molecules in models of acute and chronic cutaneous inflammation: participation of E- and P- but not L-selectin. Blood. 1999;93:580–589. - PubMed
-
- Kitayama J, Fuhlbrigge RC, Puri KD, Springer TA. P-selectin, L-selectin, and α4 integrin have distinct roles in eosinophil tethering and arrest on vascular endothelial cells under physiological flow conditions. J Immunol. 1997;159:3929–3939. - PubMed
-
- Patel KD, McEver RP. Comparison of tethering and rolling of eosinophils and neutrophils through selectins and P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1. J Immunol. 1997;159:4555–4565. - PubMed
-
- Satoh T, Kaneko M, Wu M-H, Yokozeki H, Nishioka K. Contribution of selectin ligands to eosinophil recruitment into the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32:1274–1281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

