The accumulation of oleosins determines the size of seed oilbodies in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 16877495
- PMCID: PMC1533971
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.041269
The accumulation of oleosins determines the size of seed oilbodies in Arabidopsis
Abstract
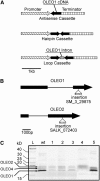
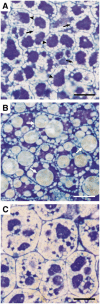
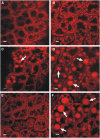
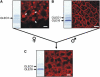
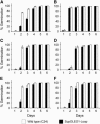
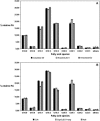
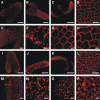
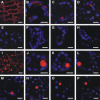
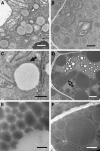
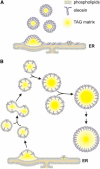
We investigated the role of the oilbody proteins in developing and germinating Arabidopsis thaliana seeds. Seed oilbodies are simple organelles comprising a matrix of triacylglycerol surrounded by a phospholipid monolayer embedded and covered with unique proteins called oleosins. Indirect observations have suggested that oleosins maintain oilbodies as small single units preventing their coalescence during seed desiccation. To understand the role of oleosins during seed development or germination, we created lines of Arabidopsis in which a major oleosin is ablated or severely attenuated. This was achieved using RNA interference techniques and through the use of a T-DNA insertional event, which appears to interrupt the major (18 kD) seed oleosin gene of Arabidopsis and results in ablation of expression. Oleosin suppression resulted in an aberrant phenotype of embryo cells that contain unusually large oilbodies that are not normally observed in seeds. Changes in the size of oilbodies caused disruption of storage organelles, altering accumulation of lipids and proteins and causing delay in germination. The aberrant phenotypes were reversed by reintroducing a recombinant oleosin. Based on this direct evidence, we have shown that oleosins are important proteins in seed tissue for controlling oilbody structure and lipid accumulation.
Figures
References
-
- Aalen, R.B., Opsahlferstad, H.G., Linnestad, C., and Olsen, O.A. (1994). Transcripts encoding an oleosin and a dormancy-related protein are present in both the aleurone layer and the embryo of developing barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seeds. Plant J. 5 385–396. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Anil, V.S., Harmon, A.C., and Rao, K.S. (2003). Temporal association of Ca(2+)-dependent protein kinase with oilbodies during seed development in Santalum album L.: Its biochemical characterization and significance. Plant Cell Physiol. 44 367–376. - PubMed
-
- Bligh, E.G., and Dyer, W.J. (1959). A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37 911–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

