Real-time detection and continuous monitoring of ER stress in vitro and in vivo by ES-TRAP: evidence for systemic, transient ER stress during endotoxemia
- PMID: 16877567
- PMCID: PMC1540736
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl515
Real-time detection and continuous monitoring of ER stress in vitro and in vivo by ES-TRAP: evidence for systemic, transient ER stress during endotoxemia
Abstract
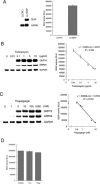
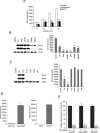
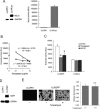
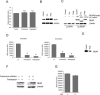
Activity of secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) produced by transfected cells is rapidly down-regulated by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress independent of transcriptional regulation. This phenomenon was observed in a wide range of cell types triggered by various ER stress inducers. The magnitude of the decrease in SEAP was proportional to the extent of ER stress and inversely correlated with the induction of endogenous ER stress markers grp78 and grp94. In contrast to SEAP, activity of secreted luciferase was less susceptible to ER stress. The decrease in SEAP activity by ER stress was caused by abnormal post-translational modification, accelerated degradation and reduced secretion of SEAP protein. In transgenic mice constitutively producing SEAP, systemic induction of ER stress led to reduction in serum SEAP. In these mice, administration with lipopolysaccharide caused rapid, transient decrease in serum SEAP activity, and it was correlated with up-regulation of grp78 in several organs including the spleen, lung, kidney, liver and heart. These results elucidated for the first time a possible involvement of transient, systemic ER stress in endotoxemia and provided evidence for usefulness of ER stress responsive alkaline phosphatase for real-time monitoring of ER stress in vitro and in vivo.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Real-time monitoring of ER stress in living cells and animals using ESTRAP assay.Methods Enzymol. 2011;490:93-106. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385114-7.00005-2. Methods Enzymol. 2011. PMID: 21266245
-
Rapid, transient induction of ER stress in the liver and kidney after acute exposure to heavy metal: evidence from transgenic sensor mice.FEBS Lett. 2007 May 15;581(10):2055-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.04.040. Epub 2007 Apr 25. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17475259
-
Secreted protein-based reporter systems for monitoring inflammatory events: critical interference by endoplasmic reticulum stress.J Immunol Methods. 2006 Aug 31;315(1-2):202-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2006.07.003. Epub 2006 Jul 31. J Immunol Methods. 2006. PMID: 16904124
-
Haptoglobin is degraded by iron in C57BL/6 mice: a possible link with endoplasmic reticulum stress.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2007 Nov-Dec;39(3):229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2007.05.008. Epub 2007 Jul 17. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2007. PMID: 17644369
-
Establishment of a non-invasive mouse reporter model for monitoring in vivo pdx-1 promoter activity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Sep 28;361(3):739-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.07.101. Epub 2007 Jul 27. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17678877
Cited by
-
Impairment of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway by methyl N-(6-phenylsulfanyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate leads to a potent cytotoxic effect in tumor cells: a novel antiproliferative agent with a potential therapeutic implication.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 31;287(36):30625-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.324228. Epub 2012 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22745125 Free PMC article.
-
Protein reporter bioassay systems for the phenotypic screening of candidate drugs: a mouse platform for anti-aging drug screening.Sensors (Basel). 2012;12(2):1648-56. doi: 10.3390/s120201648. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Sensors (Basel). 2012. PMID: 22438730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A highly sensitive assay for monitoring the secretory pathway and ER stress.PLoS One. 2007 Jun 27;2(6):e571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000571. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17593970 Free PMC article.
-
Direct, continuous monitoring of air pollution by transgenic sensor mice responsive to halogenated and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.Environ Health Perspect. 2008 Mar;116(3):349-54. doi: 10.1289/ehp.10722. Environ Health Perspect. 2008. PMID: 18335102 Free PMC article.
-
A secreted luciferase for ex vivo monitoring of in vivo processes.Nat Methods. 2008 Feb;5(2):171-3. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1177. Epub 2008 Jan 20. Nat Methods. 2008. PMID: 18204457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aridor M., Balch W.E. Integration of endoplasmic reticulum signaling in health and disease. Nature Med. 1999;5:745–751. - PubMed
-
- Schroder M., Kaufman R.J. ER stress and the unfolded protein response. Mutat. Res. 2005;569:29–63. - PubMed
-
- Kozutsumi Y., Segal M., Normington K., Gething M.J., Sambrook J. The presence of malfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum signals the induction of glucose-regulated proteins. Nature. 1988;332:462–464. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa T., Zhu H., Morishima N., Li E., Xu J., Yankner B.A., Yuan J. Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-β. Nature. 2003;403:98–103. - PubMed
-
- He H., McColl K., Distelhorst C.W. Involvement of c-Fos in signaling grp78 induction following ER calcium release. Oncogene. 2000;19:5936–5943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

