The plant-like C2 glycolate cycle and the bacterial-like glycerate pathway cooperate in phosphoglycolate metabolism in cyanobacteria
- PMID: 16877700
- PMCID: PMC1557606
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.082982
The plant-like C2 glycolate cycle and the bacterial-like glycerate pathway cooperate in phosphoglycolate metabolism in cyanobacteria
Abstract
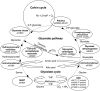
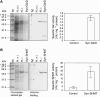
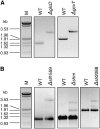
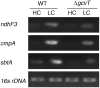
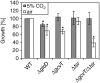
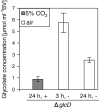
The occurrence of a photorespiratory 2-phosphoglycolate metabolism in cyanobacteria is not clear. In the genome of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803, we have identified open reading frames encoding enzymes homologous to those forming the plant-like C2 cycle and the bacterial-type glycerate pathway. To study the route and importance of 2-phosphoglycolate metabolism, the identified genes were systematically inactivated by mutagenesis. With a few exceptions, most of these genes could be inactivated without leading to a high-CO(2)-requiring phenotype. Biochemical characterization of recombinant proteins verified that Synechocystis harbors an active serine hydroxymethyltransferase, and, contrary to higher plants, expresses a glycolate dehydrogenase instead of an oxidase to convert glycolate to glyoxylate. The mutation of this enzymatic step, located prior to the branching of phosphoglycolate metabolism into the plant-like C2 cycle and the bacterial-like glycerate pathway, resulted in glycolate accumulation and a growth depression already at high CO(2). Similar growth inhibitions were found for a single mutant in the plant-type C2 cycle and more pronounced for a double mutant affected in both the C2 cycle and the glycerate pathway after cultivation at low CO(2). These results suggested that cyanobacteria metabolize phosphoglycolate by the cooperative action of the C2 cycle and the glycerate pathway. When exposed to low CO(2), glycine decarboxylase knockout mutants accumulated far more glycine and lysine than wild-type cells or mutants with inactivated glycerate pathway. This finding and the growth data imply a dominant, although not exclusive, role of the C2 route in cyanobacterial phosphoglycolate metabolism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The photorespiratory glycolate metabolism is essential for cyanobacteria and might have been conveyed endosymbiontically to plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Nov 4;105(44):17199-204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807043105. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18957552 Free PMC article.
-
Photorespiratory 2-phosphoglycolate metabolism and photoreduction of O2 cooperate in high-light acclimation of Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803.Planta. 2009 Sep;230(4):625-37. doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-0972-9. Epub 2009 Jul 4. Planta. 2009. PMID: 19578872 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of enzymes involved in the photorespiratory 2-phosphoglycolate cycle from cyanobacteria via algae toward plants.Photosynth Res. 2011 Sep;109(1-3):103-14. doi: 10.1007/s11120-010-9615-z. Epub 2011 Jan 11. Photosynth Res. 2011. PMID: 21222161
-
Photorespiratory glycolate-glyoxylate metabolism.J Exp Bot. 2016 May;67(10):3041-52. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw090. Epub 2016 Mar 19. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 26994478 Review.
-
Plant peroxisomes respire in the light: some gaps of the photorespiratory C2 cycle have become filled--others remain.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Dec;1763(12):1496-510. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.09.008. Epub 2006 Sep 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 17046077 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the oxygenase function of Form II Rubisco for production of glycolate from CO2.AMB Express. 2021 May 8;11(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13568-021-01224-6. AMB Express. 2021. PMID: 33963929 Free PMC article.
-
The Synechocystis Manganese Exporter Mnx Is Essential for Manganese Homeostasis in Cyanobacteria.Plant Physiol. 2017 Mar;173(3):1798-1810. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.01895. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Plant Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28153926 Free PMC article.
-
Photorespiration.Arabidopsis Book. 2010;8:e0130. doi: 10.1199/tab.0130. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Arabidopsis Book. 2010. PMID: 22303256 Free PMC article.
-
Distinguishing the Roles of Thylakoid Respiratory Terminal Oxidases in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Plant Physiol. 2016 Jun;171(2):1307-19. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00479. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27208274 Free PMC article.
-
Ecological genomics of marine picocyanobacteria.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009 Jun;73(2):249-99. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00035-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19487728 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Badger MR, Price GD, Long BM, Woodger FJ (2006) The environmental plasticity and ecological genomics of the cyanobacterial CO2 concentrating mechanism. J Exp Bot 57: 249–265 - PubMed
-
- Bauwe H, Kolukisaoglu U (2003) Genetic manipulation of glycine decarboxylation. J Exp Bot 54: 1523–1535 - PubMed
-
- Chang YY, Wang AY, Cronan JE Jr (1993) Molecular cloning, DNA sequencing, and biochemical analyses of Escherichia coli glyoxylate carboligase. An enzyme of the acetohydroxy acid synthase-pyruvate oxidase family. J Biol Chem 268: 3911–3919 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

