Mannose-binding lectin does not act as an acute-phase reactant in adults with community-acquired pneumococcal pneumonia
- PMID: 16879241
- PMCID: PMC1809673
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03140.x
Mannose-binding lectin does not act as an acute-phase reactant in adults with community-acquired pneumococcal pneumonia
Abstract
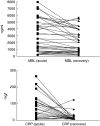
The objective of this work was to study the role of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) and C-reactive protein (CRP) in pneumococcal pneumonia, to determine whether MBL acts as an acute-phase reactant and whether the severity of the disease correlates with MBL levels. The study comprised 100 patients with pneumococcal pneumonia. The pneumonia severity score was calculated and graded into a risk class of mortality (Fine scale). The MBL genotypes and the levels of MBL and CRP at the acute and recovery phases were determined. Fifty patients with the wild-type MBL genotype showed higher MBL levels in each phase (P < 0.001) and an increased risk to developing bacteraemia, odds ratio (OR) 2.74, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.01-7.52) (P = 0.02), but this did not correlate with the pneumonia severity class. CRP levels in the acute phase, 79.53 mg/l [standard deviation (s.d.) 106.93], were higher in the subjects with positive blood cultures (P = 0.003), and remained higher [20.12 mg/l (s.d. 31.90)] in the group of patients with an underlying disease (P = 0.01). No correlation was observed between the levels of MBL and CRP in each phase, or with the pneumonia severity score. We cannot conclude that MBL acts uniformly as an acute-phase reactant in pneumococcal pneumonia. MBL levels do not correlate well with the severity of the pneumonia. The risk of developing bacteraemia could be enhanced in individuals with the wild-type MBL genotype.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mannose-binding lectin and mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease 2 in susceptibility, severity, and outcome of pneumonia in adults.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008 Aug;122(2):368-74, 374.e1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.05.037. Epub 2008 Jun 25. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18582923
-
The role of mannose-binding lectin in pneumococcal infection.Eur Respir J. 2013 Jan;41(1):131-9. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00174111. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Eur Respir J. 2013. PMID: 22523362
-
Mannose-binding lectin genotypes in susceptibility to community-acquired pneumonia.Chest. 2008 Dec;134(6):1135-1140. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-0642. Epub 2008 Jul 18. Chest. 2008. PMID: 18641104
-
Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalisation. Factors of importance for the short-and long term prognosis.Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1995;97:1-60. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1995. PMID: 8584866 Review.
-
High Expression of Mannose-Binding Lectin and the Risk of Vascular Complications of Diabetes: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2015 Jul;17(7):490-7. doi: 10.1089/dia.2014.0372. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25756786 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute-phase responsiveness of mannose-binding lectin in community-acquired pneumonia is highly dependent upon MBL2 genotypes.Clin Exp Immunol. 2009 Jun;156(3):488-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03929.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19438602 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating mannan-binding lectin, M-, L-, H-ficolin and collectin-liver-1 levels in patients with acute liver failure.Liver Int. 2015 Mar;35(3):756-63. doi: 10.1111/liv.12682. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 25203057 Free PMC article.
-
Low Levels of Immunoglobulins and Mannose-Binding Lectin Are Not Associated With Etiology, Severity, or Outcome in Community-Acquired Pneumonia.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2018 Jan 5;5(2):ofy002. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofy002. eCollection 2018 Feb. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29410975 Free PMC article.
-
AIDS patients have increased surfactant protein D but normal mannose binding lectin levels in lung fluid.Respir Res. 2007 Jun 13;8(1):42. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-8-42. Respir Res. 2007. PMID: 17567900 Free PMC article.
-
Host genetic variability and pneumococcal disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Genomics. 2019 Sep 13;12(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12920-019-0572-x. BMC Med Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31519222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almirall J, Bolibar I, Vidal J, et al. Epidemiology of community-acquired pneumonia in adults: a population based study. Eur Resp J. 2000;15:757–63. - PubMed
-
- Castell JV, Gomez-Lechon MJ, David M, Fabra R, Trullen R, Heinrich PC. Acute-phase response of human hepatocytes: regulation of acute-phase protein synthesis by interleukin-6. Hepatology. 1990;12:1179–86. - PubMed
-
- Szalai AJ, Agrawal A, Greenhough TJ, Volanakis JE. C-reactive protein: structural biology, gene expression and host defense function. Immunol Res. 1997;16:127–36. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan MH, Volanakis JE. Interaction of C-reactive protein complexes with the complement system. I. Consumption of human complement associated with the reaction of C-reactive protein with pneumococcal C polysaccharide and the choline phosphatides, lecitin and sphingomyelin. J Immunol. 1974;112:2135–47. - PubMed
-
- Ortqvist A, Hedlund J, Wretlind B, Carlstrom A, Kalin M. Diagnostic and prognostic value of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in community-acquired pneumonia. Scand J Infect Dis. 1995;27:457–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous