CD134 expression on CD4+ T cells is associated with nephritis and disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 16879242
- PMCID: PMC1809690
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03141.x
CD134 expression on CD4+ T cells is associated with nephritis and disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
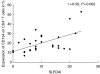
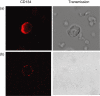
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is characterized by a deviation of the immune system that involves T cell-dependent autoantibody production. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of co-stimulatory markers on T cells in this disease. Twenty-eight patients with SLE as defined by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria and 11 healthy controls were included into the study. Eleven patients had biopsy-proven lupus nephritis while 17 patients had no clinical evidence of lupus nephritis. Clinical disease activity was assessed according to the systemic lupus erythematosus disease index (SLEDAI). CD4+ T cell populations in the peripheral blood were analysed for the expression of co-stimulatory markers CD45RO, CD70, CD80, CD86, CD137, CD137L, CD134, CD152, CD154 and ICOS. SLE patients showed an increased frequency of peripheral CD4+ T cells expressing high levels of CD80, CD86 and CD134 compared to healthy controls (7.1 +/- 1.5% versus 1.7 +/- 0.9%; P < 0.005; 2.3 +/- 0.4% versus 1.0 +/- 0.2%; P = 0.008, 20.2 +/- 2.0% versus 10.6 +/- 1.9%; P < 0.005, respectively). Significantly higher levels of CD80 on CD4+ T cells were detected in SLE patients with lupus nephritis compared to patients without nephritis (11.9 +/- 3.3% versus 4.0 +/- 0.7%; P < 0.005). There was an increased presence of CD134+ CD4+ cells in SLE patients with lupus nephritis (27.5 +/- 4.0% versus 15.5 +/- 1.3%; P < 0.005). CD80 and CD134 expression was significantly correlated with SLEDAI (r = 0.42, P = 0.03; r = 0.56, P < 0.005). Co-stimulatory molecules on CD4+ T cells are associated with renal disease and disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures
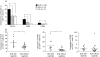
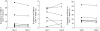
Similar articles
-
Peripheral circulating activated b-cell populations are associated with nephritis and disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Scand J Immunol. 2007 Nov;66(5):584-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2007.02008.x. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Scand J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17868260
-
[Expression and clinical significance of inducible co-stimulator on peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Feb 2;85(5):318-23. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15854508 Chinese.
-
Activation-associated phenotype of CD3 T cells in acute graft-versus-host disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Jul;145(1):36-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03104.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16792671 Free PMC article.
-
The Progress of Investigating the CD137-CD137L Axis as a Potential Target for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Cells. 2019 Sep 6;8(9):1044. doi: 10.3390/cells8091044. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31500130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of CD4 T cell memory by OX40 (CD134).Vaccine. 2006 Feb 13;24(7):872-83. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.07.108. Epub 2005 Sep 7. Vaccine. 2006. PMID: 16176850 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of the co-stimulator OX40L with systemic lupus erythematosus.J Mol Med (Berl). 2009 Mar;87(3):229-34. doi: 10.1007/s00109-008-0431-2. Epub 2008 Dec 16. J Mol Med (Berl). 2009. PMID: 19083191 Review.
-
Current and novel therapeutics in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Feb;127(2):303-12; quiz 313-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.12.1087. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21281862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The tumour necrosis factor/TNF receptor superfamily: therapeutic targets in autoimmune diseases.Clin Exp Immunol. 2011 May;164(2):145-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04375.x. Epub 2011 Mar 14. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21401577 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of costimulatory markers CD134 and CD80 on interleukin-17 producing T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):R150. doi: 10.1186/ar3100. Epub 2010 Jul 23. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20653937 Free PMC article.
-
OX40, OX40L and Autoimmunity: a Comprehensive Review.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016 Jun;50(3):312-32. doi: 10.1007/s12016-015-8498-3. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26215166 Review.
References
-
- Watts TH, DeBenedette MA. T cell co-stimulatory molecules other than CD28. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999;11:286–93. - PubMed
-
- Finney HM, Akbar AN, Lawson AD. Activation of resting human primary T cells with chimeric receptors. co-stimulation from CD28, inducible co-stimulator, CD134, and CD137 in series with signals from the TCR zeta chain. J Immunol. 2004;172:104–13. - PubMed
-
- Liang B, Kashgarian MJ, Sharpe AH, et al. Autoantibody responses and pathology regulated by B7-1 and B7-2 co-stimulation in MRL/lpr lupus. J Immunol. 2000;165:3436–43. - PubMed
-
- Kinoshita K, Tesch G, Schwarting A, et al. Costimulation by B7-1 and B7-2 is required for autoimmune disease in MRL-Faslpr mice. J Immunol. 2000;164:6046–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

