Inhibition of oxidative stress and cytokine activity by curcumin in amelioration of endotoxin-induced experimental hepatoxicity in rodents
- PMID: 16879252
- PMCID: PMC1809677
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03108.x
Inhibition of oxidative stress and cytokine activity by curcumin in amelioration of endotoxin-induced experimental hepatoxicity in rodents
Abstract
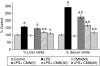
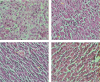
The present study is aimed at investigating the effect of curcumin (CMN) in salvaging endotoxin-induced hepatic dysfunction and oxidative stress in the liver of rodents. Hepatotoxicity was induced by administering lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in a single dose of 1 mg/kg intraperitoneally to the animals, which were being treated with CMN daily for 7 days. Liver enzymes serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP), total bilirubin and total protein were estimated in serum. Oxidative stress in liver tissue homogenates was estimated by measuring thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), glutathione (GSH) content and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Serum and tissue nitrite was estimated using Greiss reagent and served as an indicator of NO production. A separate set of experiments was performed to estimate the effect of CMN on cytokine levels in mouse serum after LPS challenge. LPS induced a marked hepatic dysfunction evident by rise in serum levels of ALT, AST, ALP and total bilirubin (P < 0.05). TBARS levels were significantly increased, whereas GSH and SOD levels decreased in the liver homogenates of LPS-challenged rats. CMN administration attenuated these effects of LPS successfully. Further CMN treatment also regressed various structural changes induced by LPS in the livers of rats and decreased the levels of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in mouse plasma. In conclusion, these findings suggest that CMN attenuates LPS-induced hepatotoxicity possibly by preventing cytotoxic effects of NO, oxygen free radicals and cytokines.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beneficial effect of hesperidin on lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatotoxicity.Toxicology. 2006 Sep 21;226(2-3):152-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.06.018. Epub 2006 Jul 7. Toxicology. 2006. PMID: 16919860
-
Curcumin, a diferuloylmethane, attenuates cyclosporine-induced renal dysfunction and oxidative stress in rat kidneys.BMC Pharmacol. 2005 Oct 15;5:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2210-5-15. BMC Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16225695 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of Vitamin E pre-treatment on N-nitrosodiethylamine induced oxidative stress in rat liver.Chem Biol Interact. 2005 Oct 20;156(2-3):101-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2005.08.001. Chem Biol Interact. 2005. PMID: 16144695
-
Comparative effects of curcumin and resveratrol on aflatoxin B(1)-induced liver injury in rats.Arch Toxicol. 2010 May;84(5):389-96. doi: 10.1007/s00204-010-0511-2. Epub 2010 Jan 30. Arch Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20112103
-
Sesame oil protects against lipopolysaccharide-stimulated oxidative stress in rats.Crit Care Med. 2004 Jan;32(1):227-31. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000104947.16669.29. Crit Care Med. 2004. PMID: 14707583
Cited by
-
Protective effects of ulinastatin on acute liver failure induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine.Dig Dis Sci. 2012 Feb;57(2):399-404. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1927-0. Epub 2011 Oct 15. Dig Dis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22001939
-
Efficacy of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) in skin B16-F0 melanoma tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice.Tumour Biol. 2014 May;35(5):4967-76. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-1654-1. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24492939
-
Alcohol metabolites and lipopolysaccharide: roles in the development and/or progression of alcoholic liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Mar 14;15(10):1209-18. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1209. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19291821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin and Health.Molecules. 2016 Feb 25;21(3):264. doi: 10.3390/molecules21030264. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 26927041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural polyphenols for the prevention of irritable bowel syndrome: molecular mechanisms and targets; a comprehensive review.Daru. 2019 Dec;27(2):755-780. doi: 10.1007/s40199-019-00284-1. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Daru. 2019. PMID: 31273572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hartung T, Tiegs G, Wendel A. The role of leukotriene D4 in septic shock models. Eicosanoids. 1992;5(Suppl):S42–4. - PubMed
-
- James PE, Madhani M, Roebuck W, Jackson SK, Swartz HM. Endotoxin-induced liver hypoxia: defective oxygen delivery versus oxygen consumption. Nitric Oxide. 2002;6:18–28. - PubMed
-
- Su GL. Lipopolysaccharides in liver injury: molecular mechanisms of Kupffer cell activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002;283:G256–65. - PubMed
-
- Hines IN, Wheeler MD. Recent advances in alcoholic liver disease III. Role of the innate immune response in alcoholic hepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;287:G310–4. - PubMed
-
- Luster MI, Germolec DR, Yoshida T, Kayama F, Thompson M. Endotoxin-induced cytokine gene expression and excretion in the liver. Hepatology. 1994;19:480–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

