Autoimmunity to type VII collagen in SKH1 mice is independent of regulatory T cells
- PMID: 16879253
- PMCID: PMC1809679
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03115.x
Autoimmunity to type VII collagen in SKH1 mice is independent of regulatory T cells
Abstract
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita is an autoimmune blistering disease characterized by circulating and skin basement membrane-bound IgG autoantibodies to type VII collagen, a major structural protein of the dermal-epidermal junction. Regulatory T cells (T(reg)) suppress self antigen-mediated autoimmune responses. To investigate the role of T(reg) in the the autoimmune response to type VII collagen in a mouse model, a monoclonal antibody against mouse CD25 was used to deplete T(reg). A recombinant mouse type VII collagen NC1 domain protein and mouse albumin were used as antigens. SKH1 mice were used as a testing host. Group 1 mice received NC1 immunization and were functionally depleted of T(reg); group 2 mice received NC1 immunization and rat isotype control; and group 3 mice received albumin immunization and were functionally depleted of T(reg). Results demonstrated that anti-NC1 IgG autoantibodies with high titres, as determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western blotting, developed in all mice immunized with NC1 (groups 1 and 2), but were undetected in group 3 mice. The predominant subclasses of anti-NC1 autoantibodies were IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b; furthermore, these antibodies carried only the kappa light chain. IgG autoantibodies in the sera of NC1-immunized mice reacted with mouse skin basement membrane in vitro and deposited in skin basement membrane in vivo as detected by indirect and direct immunofluorescence microscopy, respectively. Our data suggest that the development of autoimmunity against type VII collagen in mice is independent of T(reg) function and the autoimmune response is mediated by both Th1 and Th2 cells. We speculate that the basement membrane deposition of IgG may eventually lead to blister development.
Figures

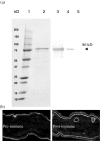
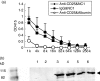


Similar articles
-
Induction of experimental epidermolysis bullosa acquisita by immunization with murine collagen VII.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;961:371-87. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-227-8_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23325658
-
T and B cells target identical regions of the non-collagenous domain 1 of type VII collagen in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita.Clin Immunol. 2010 Apr;135(1):99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2009.12.010. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20093095
-
T cells are required for the production of blister-inducing autoantibodies in experimental epidermolysis bullosa acquisita.J Immunol. 2010 Feb 1;184(3):1596-603. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901412. Epub 2009 Dec 28. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20038644
-
Childhood epidermolysis bullosa acquisita with autoantibodies against the noncollagenous 1 and 2 domains of type VII collagen: case report and review of the literature.Br J Dermatol. 2006 Nov;155(5):1048-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07443.x. Br J Dermatol. 2006. PMID: 17034540 Review.
-
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: what's new?J Dermatol. 2010 Mar;37(3):220-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00799.x. J Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20507385 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita-Current and Emerging Treatments.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 1;12(3):1139. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031139. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blister-inducing antibodies target multiple epitopes on collagen VII in mice.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Sep;18(9):1727-39. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12338. Epub 2014 Aug 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 25091020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Woodley DT, Briggaman RA, O’Keefe EJ, Inman AO, Queen LL, Gammon WR. Identification of the skin basement-membrane autoantigen in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. N Engl J Med. 1984;310:1007–13. - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Chan LS, Cai X, O'Toole EA, Sample JC, Woodley DT. Development of an ELISA for rapid detection of anti-type VII collagen autoantibodies in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. J Invest Dermatol. 1997;108:68–72. - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Keene DR, Costa FK, Tahk SH, Woodley DT. The carboxyl terminus of type VII collagen mediates antiparallel dimer formation and constitutes a new antigenic epitope for epidermolysis bullosa acquisita autoantibodies. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:21649–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

