T-bet negatively regulates autoimmune myocarditis by suppressing local production of interleukin 17
- PMID: 16880257
- PMCID: PMC2118365
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20052222
T-bet negatively regulates autoimmune myocarditis by suppressing local production of interleukin 17
Abstract
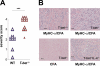
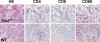
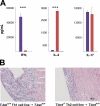
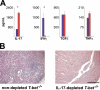
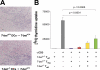
Experimental autoimmune myocarditis (EAM) appears after infectious heart disease, the most common cause of dilated cardiomyopathy in humans. Here we report that mice lacking T-bet, a T-box transcription factor required for T helper (Th)1 cell differentiation and interferon (IFN)-gamma production, develop severe autoimmune heart disease compared to T-bet+/+ control mice. Experiments in T-bet-/- IL-4-/- and T-bet-/- IL-4Ralpha-/- mice, as well as transfer of heart-specific Th1 and Th2 cell lines, showed that autoimmune heart disease develops independently of Th1 or Th2 polarization. Analysis of T-bet-/- IL-12Rbeta1-/- and T-bet-/- IL-12p35-/- mice then identified interleukin (IL)-23 as critical for EAM pathogenesis. In addition, T-bet-/- mice showed a marked increase in production of the IL-23-dependent cytokine IL-17 by heart-infiltrating lymphocytes, and in vivo IL-17 depletion markedly reduced EAM severity in T-bet-/- mice. Heart-infiltrating T-bet-/- CD8+ but not CD8- T cells secrete IFN-gamma, which inhibits IL-17 production and protects against severe EAM. In contrast, T-bet-/- CD8+ lymphocytes completely lost their capacity to release IFN-gamma within the heart. Collectively, these data show that severe IL-17-mediated EAM can develop in the absence of T-bet, and that T-bet can regulate autoimmunity via the control of nonspecific CD8+ T cell bystander functions in the inflamed target organ.
Figures
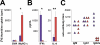

References
-
- Eriksson, U., and J.M. Penninger. 2005. Autoimmune heart failure: new understandings of pathogenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 37:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Koelsch, S.P.S., G. Hufnagel, and B. Maisch. 2004. The European study of epidemiology and treatment of cardiac inflammatory diseases (ESETCID)—epidemiological results after 6 years. In Annual Meeting of the AHA, New Orleans.
-
- Caforio, A.L., E. Bonifacio, J.T. Stewart, D. Neglia, O. Parodi, G.F. Bottazzo, and W.J. McKenna. 1990. Novel organ-specific circulating cardiac autoantibodies in dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 15:1527–1534. - PubMed
-
- Frustaci, A., C. Chimenti, F. Calabrese, M. Pieroni, G. Thiene, and A. Maseri. 2003. Immunosuppressive therapy for active lymphocytic myocarditis: virological and immunologic profile of responders versus nonresponders. Circulation. 107:857–863. - PubMed
-
- Omerovic, E., E. Bollano, B. Andersson, V. Kujacic, W. Schulze, A. Hjalmarson, F. Waagstein, and M. Fu. 2000. Induction of cardiomyopathy in severe combined immunodeficiency mice by transfer of lymphocytes from patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Autoimmunity. 32:271–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

