Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate [PtdIns3P] is generated at the plasma membrane by an inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase: endogenous PtdIns3P can promote GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane
- PMID: 16880518
- PMCID: PMC1592800
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00203-06
Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate [PtdIns3P] is generated at the plasma membrane by an inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase: endogenous PtdIns3P can promote GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane
Abstract
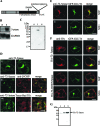
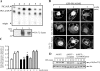
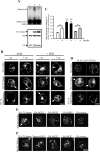
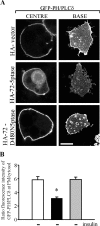
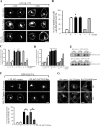
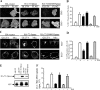
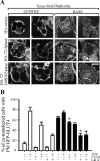
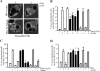
Exogenous delivery of carrier-linked phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate [PtdIns(3)P] to adipocytes promotes the trafficking, but not the insertion, of the glucose transporter GLUT4 into the plasma membrane. However, it is yet to be demonstrated if endogenous PtdIns(3)P regulates GLUT4 trafficking and, in addition, the metabolic pathways mediating plasma membrane PtdIns(3)P synthesis are uncharacterized. In unstimulated 3T3-L1 adipocytes, conditions under which PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 was not synthesized, ectopic expression of wild-type, but not catalytically inactive 72-kDa inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase (72-5ptase), generated PtdIns(3)P at the plasma membrane. Immunoprecipitated 72-5ptase from adipocytes hydrolyzed PtdIns(3,5)P2, forming PtdIns(3)P. Overexpression of the 72-5ptase was used to functionally dissect the role of endogenous PtdIns(3)P in GLUT4 translocation and/or plasma membrane insertion. In unstimulated adipocytes wild type, but not catalytically inactive, 72-5ptase, promoted GLUT4 translocation and insertion into the plasma membrane but not glucose uptake. Overexpression of FLAG-2xFYVE/Hrs, which binds and sequesters PtdIns(3)P, blocked 72-5ptase-induced GLUT4 translocation. Actin monomer binding, using latrunculin A treatment, also blocked 72-5ptase-stimulated GLUT4 translocation. 72-5ptase expression promoted GLUT4 trafficking via a Rab11-dependent pathway but not by Rab5-mediated endocytosis. Therefore, endogenous PtdIns(3)P at the plasma membrane promotes GLUT4 translocation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An SH2 domain-containing 5' inositolphosphatase inhibits insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation and growth factor-induced actin filament rearrangement.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;19(2):1081-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.1081. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9891043 Free PMC article.
-
Role for a novel signaling intermediate, phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, in insulin-regulated F-actin stress fiber breakdown and GLUT4 translocation.Endocrinology. 2004 Nov;145(11):4853-65. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0489. Epub 2004 Jul 29. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15284192
-
The type Ialpha inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase generates and terminates phosphoinositide 3-kinase signals on endosomes and the plasma membrane.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 May;16(5):2218-33. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0799. Epub 2005 Feb 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15716355 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3/Akt signalling by inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Feb;44(1):240-52. doi: 10.1042/BST20150214. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 26862211 Review.
-
The role of the inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases in cellular function and human disease.Biochem J. 2009 Apr 1;419(1):29-49. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081673. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19272022 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin stimulates phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate production via the activation of Rab5.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Jul;19(7):2718-28. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-01-0105. Epub 2008 Apr 23. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18434594 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoinositides in insulin action on GLUT4 dynamics: not just PtdIns(3,4,5)P3.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Sep;295(3):E536-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90353.2008. Epub 2008 May 20. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 18492765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoinositides: tiny lipids with giant impact on cell regulation.Physiol Rev. 2013 Jul;93(3):1019-137. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00028.2012. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23899561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of P-Rex1 as a novel Rac1-guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that promotes actin remodeling and GLUT4 protein trafficking in adipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 16;286(50):43229-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.306621. Epub 2011 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22002247 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoinositides: Key modulators of energy metabolism.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1851(6):857-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.11.008. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25463477 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abramoff, M., P. Magelhaes, and S. Ram. 2004. Image processing with Image J. Biophotonics Int. 11:36-42.
-
- Al-Hasani, H., C. S. Hinck, and S. W. Cushman. 1998. Endocytosis of the glucose transporter GLUT4 is mediated by the GTPase dynamin. J. Biol. Chem. 273:17504-17510. - PubMed
-
- Asano, T., A. Kanda, H. Katagiri, M. Nawano, T. Ogihara, K. Inukai, M. Anai, Y. Fukushima, Y. Yazaki, M. Kikuchi, R. Hooshmand-Rad, C. H. Heldin, Y. Oka, and M. Funaki. 2000. p110beta is up-regulated during differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells and contributes to the highly insulin-responsive glucose transport activity. J. Biol. Chem. 275:17671-17676. - PubMed
-
- Asano, T., Y. Mochizuki, K. Matsumoto, T. Takenawa, and T. Endo. 1999. Pharbin, a novel inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase, induces dendritic appearances in fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 261:188-195. - PubMed
-
- Backer, J. M. 2000. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases and the regulation of vesicular trafficking. Mol. Cell. Biol. Res. Commun. 3:193-204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
