CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP) regulates osteoblast differentiation
- PMID: 16880521
- PMCID: PMC1592788
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02429-05
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP) regulates osteoblast differentiation
Abstract
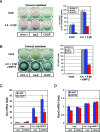
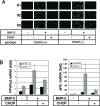
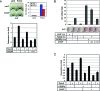
Differentiation of committed osteoblasts is controlled by complex activities involving signal transduction and gene expression, and Runx2 and Osterix function as master regulators for this process. Recently, CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBPs) have been reported to regulate osteogenesis in addition to adipogenesis. However, the roles of C/EBP transcription factors in the control of osteoblast differentiation have yet to be fully elucidated. Here we show that C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP; also known as C/EBPzeta) is expressed in bone as well as in mesenchymal progenitors and primary osteoblasts. Overexpression of CHOP reduces alkaline phosphatase activity in primary osteoblasts and suppresses the formation of calcified bone nodules. CHOP-deficient osteoblasts differentiate more strongly than their wild-type counterparts, suggesting that endogenous CHOP plays an important role in the inhibition of osteoblast differentiation. Furthermore, endogenous CHOP induces differentiation of calvarial osteoblasts upon bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) treatment. CHOP forms heterodimers with C/EBPbeta and inhibits the DNA-binding activity as well as Runx2-binding activity of C/EBPbeta, leading to inhibition of osteocalcin gene transcription. These findings indicate that CHOP acts as a dominant-negative inhibitor of C/EBPbeta and prevents osteoblast differentiation but promotes BMP signaling in a cell-type-dependent manner. Thus, endogenous CHOP may have dual roles in regulating osteoblast differentiation and bone formation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta activates the Runx2-mediated transcription of mouse osteocalcin II promoter.J Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Jun;36(3):531-46. doi: 10.1677/jme.1.01944. J Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16720721
-
A CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta isoform, liver-enriched inhibitory protein, regulates commitment of osteoblasts and adipocytes.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Mar;25(5):1971-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.5.1971-1979.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15713650 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential modifiers of Runx2/Cbfa1 activity in C2C12 cells in response to bone morphogenetic protein-7.Cells Tissues Organs. 2004;176(1-3):28-40. doi: 10.1159/000075025. Cells Tissues Organs. 2004. PMID: 14745233
-
The developmental control of osteoblast-specific gene expression: role of specific transcription factors and the extracellular matrix environment.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1999;10(1):40-57. doi: 10.1177/10454411990100010201. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1999. PMID: 10759426 Review.
-
[Bone and calcium update; bone research update. Regulatory mechanisms in osteoblast differentiation].Clin Calcium. 2011 Dec;21(12):103-12. Clin Calcium. 2011. PMID: 22133830 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Differential regulation of CHOP-10/GADD153 gene expression by MAPK signaling in pancreatic beta-cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jul 10;104(28):11518-25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704618104. Epub 2007 Jul 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17615236 Free PMC article.
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta promotes osteoblast differentiation by enhancing Runx2 activity with ATF4.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Dec;19(12):5373-86. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-03-0329. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18843047 Free PMC article.
-
DDIT3 overexpression increases odontoblastic potential of human dental pulp cells.Cell Prolif. 2014 Jun;47(3):249-57. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12104. Epub 2014 Apr 16. Cell Prolif. 2014. PMID: 24738922 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of osteoblastic Arl6ip5 impaired osteoblast differentiation and enhanced osteoclastogenesis via disturbance of ER calcium homeostasis and induction of ER stress-mediated apoptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Oct 16;5(10):e1464. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.427. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25321471 Free PMC article.
-
Misexpression of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta causes osteopenia.J Endocrinol. 2009 May;201(2):263-74. doi: 10.1677/JOE-08-0514. Epub 2009 Feb 13. J Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19218285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachner, D., M. Ahrens, D. Schroder, A. Hoffmann, J. Lauder, N. Betat, P. Steinert, L. Flohe, and G. Gross. 1998. Bmp-2 downstream targets in mesenchymal development identified by subtractive cloning from recombinant mesenchymal progenitors (C3H10T1/2). Dev. Dyn. 213:398-411. - PubMed
-
- Barone, M. V., A. Crozat, A. Tabaee, L. Philipson, and D. Ron. 1994. CHOP (GADD153) and its oncogenic variant, TLS-CHOP, have opposing effects on the induction of G1/S arrest. Genes Dev. 15:453-464. - PubMed
-
- Ducy, P., R. Zhang, V. Geoffroy, A. L. Ridall, and G. Karsenty. 1997. Osf2/Cbfa1: a transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation. Cell 89:747-754. - PubMed
-
- Ebisawa, T., M. Fukuchi, G. Murakami, T. Chiba, K. Tanaka, T. Imamura, and K. Miyazono. 2001. Smurf1 interacts with transforming growth factor-β type I receptor through Smad7 and induces receptor degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 276:12477-12480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
