Functional spliceosomal A complexes can be assembled in vitro in the absence of a penta-snRNP
- PMID: 16880538
- PMCID: PMC1557700
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.120606
Functional spliceosomal A complexes can be assembled in vitro in the absence of a penta-snRNP
Abstract
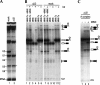
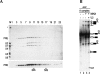
Two different models currently exist for the assembly pathway of the spliceosome, namely, the traditional model, in which spliceosomal snRNPs associate in a stepwise, ordered manner with the pre-mRNA, and the holospliceosome model, in which all spliceosomal snRNPs preassemble into a penta-snRNP complex. Here we have tested whether the spliceosomal A complex, which contains solely U1 and U2 snRNPs bound to pre-mRNA, is a functional, bona fide assembly intermediate. Significantly, A complexes affinity-purified from nuclear extract depleted of U4/U6 snRNPs (and thus unable to form a penta-snRNP) supported pre-mRNA splicing in nuclear extract depleted of U2 snRNPs, whereas naked pre-mRNA did not. Mixing experiments with purified A complexes and naked pre-mRNA additionally confirmed that under these conditions, A complexes do not form de novo. Thus, our studies demonstrate that holospliceosome formation is not a prerequisite for generating catalytically active spliceosomes and that, at least in vitro, the U1 and U2 snRNPs can functionally associate with the pre-mRNA, prior to and independent of the tri-snRNP. The ability to isolate functional spliceosomal A complexes paves the way to study in detail subsequent spliceosome assembly steps using purified components.
Figures

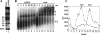
References
-
- Ast G. How did alternative splicing evolve? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004;5:773–782. - PubMed
-
- Bach M., Bringmann P., Lührmann R. Purification of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles with antibodies against modified nucleosides of small nuclear RNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1990;181:232–257. - PubMed
-
- Barabino S.M., Blencowe B.J., Ryder U., Sproat B.S., Lamond A.I. Targeted snRNP depletion reveals an additional role for mammalian U1 snRNP in spliceosome assembly. Cell. 1990;63:293–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
