MAPK signalling: ERK5 versus ERK1/2
- PMID: 16880823
- PMCID: PMC1525153
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400755
MAPK signalling: ERK5 versus ERK1/2
Abstract
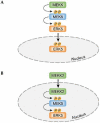
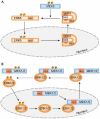
Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) is a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family and, similar to ERK1/2, has the Thr-Glu-Tyr (TEY) activation motif. Both ERK5 and ERK1/2 are activated by growth factors and have an important role in the regulation of cell proliferation and cell differentiation. Moreover, both the ERK5 and the ERK1/2 pathways are sensitive to PD98059 and U0126, which are two well-known inhibitors of the ERK pathway. Despite these similarities, recent studies have revealed distinctive features of the ERK5 pathway: ERK5 has a key role in cardiovascular development and neural differentiation; ERK5 nuclear translocation is controlled by its own nuclear localizing and nuclear export activities; and the carboxy-terminal half of ERK5, which follows its kinase catalytic domain, has a unique function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cell-cycle arrest by PD184352 requires inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) 1/2 but not ERK5/BMK1.Biochem J. 2002 Sep 1;366(Pt 2):673-80. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020372. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12069688 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of either ERK1/2 or ERK5 MAP kinase pathways can lead to disruption of the actin cytoskeleton.J Cell Sci. 2005 Apr 15;118(Pt 8):1663-71. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02308. Epub 2005 Mar 29. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15797923
-
Differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 and ERK5 by neurotrophins, neuronal activity, and cAMP in neurons.J Neurosci. 2001 Jan 15;21(2):434-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-02-00434.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11160424 Free PMC article.
-
ERK5: structure, regulation and function.Cell Signal. 2012 Nov;24(11):2187-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.07.007. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22800864 Review.
-
ERK 5/MAPK pathway has a major role in 1α,25-(OH)2 vitamin D3-induced terminal differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Oct;144 Pt A:223-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 26. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24514755 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse and converging roles of ERK1/2 and ERK5 pathways on mesenchymal to epithelial transition in breast cancer.Transl Oncol. 2021 Jun;14(6):101046. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101046. Epub 2021 Mar 21. Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33761370 Free PMC article.
-
Tie1 deficiency induces endothelial-mesenchymal transition.EMBO Rep. 2012 May 1;13(5):431-9. doi: 10.1038/embor.2012.29. EMBO Rep. 2012. PMID: 22421998 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological effects of higenamine based on signalling pathways and mechanism of action.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;13:981048. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.981048. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of microRNAs-143 and -145 in B-cell malignancies.Cancer Sci. 2007 Dec;98(12):1914-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00618.x. Epub 2007 Sep 24. Cancer Sci. 2007. PMID: 17892514 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a Read-through Fusion Transcript, BCL2L2-PABPN1, Involved in Porcine Adipogenesis.Genes (Basel). 2022 Feb 28;13(3):445. doi: 10.3390/genes13030445. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35327999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe J, Kusuhara M, Ulevitch RJ, Berk BC, Lee JD (1996) Big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (BMK1) is a redox-sensitive kinase. J Biol Chem 271: 16586–16590 - PubMed
-
- Akaike M, Che W, Marmarosh NL, Ohta S, Osawa M, Ding B, Berk BC, Yan C, Abe J (2004) The hinge-helix 1 region of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ1 (PPARγ1) mediates interaction with extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 and PPARγ1 transcriptional activation: involvement in flow-induced PPARγ activation in endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol 24: 8691–8704 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

