Transzygomatic-Subtemporal Approach for Middle Meningeal-to-P2 Segment of the Posterior Cerebral Artery Bypass: An Anatomical and Technical Study
- PMID: 16880900
- PMCID: PMC1408075
- DOI: 10.1055/s-2006-931622
Transzygomatic-Subtemporal Approach for Middle Meningeal-to-P2 Segment of the Posterior Cerebral Artery Bypass: An Anatomical and Technical Study
Abstract
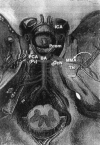
We evaluated the use of a bypass between the middle meningeal artery (MMA) and P2 segment of the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) as an alternative to an external carotid artery (ECA-to-PCA) anastomosis. Five adult cadaveric heads (10 sides) were used. After a temporal craniotomy and zygomatic arch osteotomy were performed, the dura of the floor of the middle cranial fossa was separated and elevated. The MMA was dissected away from the dura until the foramen spinosum was reached. Intradurally, the carotid and sylvian cisterns were opened. After the temporal lobe was retracted, the interpeduncular and ambient cisterns were opened and the P2 segment of the PCA was exposed. The MMA trunk was transsected just before the bifurcation of its anterior and posterior branches where it passes inside the dura and over the foramen spinosum. It was anastomosed end to side with the P2 segment of the PCA. The mean caliber of the MMA trunk before its bifurcation was 2.1 +/- 0.25 mm, and the mean caliber of the P2 was 2.2 +/- 0.2 mm. The mean length of the MMA used to perform the bypass was 32 +/- 4.1 mm, and the mean length of the MMA trunk was 39.5 +/- 4.4 mm. This bypass procedure is simpler to perform than an ECA-to-P2 revascularization using long grafts. The caliber and length of the MMA trunk are suitable to provide sufficient blood flow. Furthermore, the course of the bypass is straight.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proximal STA to proximal PCA bypass using a radial artery graft by posterior oblique transzygomatic subtemporal approach.Neurosurg Rev. 2009 Jan;32(1):95-9; discussion 99. doi: 10.1007/s10143-008-0157-1. Epub 2008 Sep 5. Neurosurg Rev. 2009. PMID: 18773233
-
Distal superficial temporal artery to proximal posterior cerebral artery bypass by posterior oblique transzygomatic subtemporal approach.Skull Base. 2010 Nov;20(6):415-20. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1254405. Skull Base. 2010. PMID: 21772798 Free PMC article.
-
A modified technique for bypass of the external carotid artery to the proximal posterior cerebral artery: an anatomical and technical study.Acta Otolaryngol. 2006 May;126(5):526-9. doi: 10.1080/00016480500401050. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006. PMID: 16698704
-
The transzygomatic approach.J Clin Neurosci. 2010 Nov;17(11):1428-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2010.03.023. Epub 2010 Aug 6. J Clin Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20692168 Review.
-
Anomalous branching of the middle meningeal artery from the basilar artery: a systematic review.Front Neurol. 2024 Jan 23;14:1301426. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1301426. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38322796 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transfacial Surgical Approaches to Secure Wide Exposure of the Skull Base.Arch Craniofac Surg. 2015 Apr;16(1):17-23. doi: 10.7181/acfs.2015.16.1.17. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2015. PMID: 28913213 Free PMC article.
-
Morphometric analysis of the middle meningeal artery organization in humans-embryological considerations.J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2013 Apr;74(2):108-12. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1333615. Epub 2013 Jan 22. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2013. PMID: 24436897 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormality of the Foramen Spinosum due to a Variation in the Trajectory of the Middle Meningeal Artery: A Case Report in Human.J Neurol Surg Rep. 2013 Dec;74(2):73-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1347901. Epub 2013 May 23. J Neurol Surg Rep. 2013. PMID: 24294564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausman J I, Diaz F G, de los Reyes R A, et al. Posterior circulation revascularisation. Superficial temporal artery to superior cerebellar artery anastomosis. J Neurosurg. 1982;56:766–776. - PubMed
-
- Heros R C, Ameri A M. Rupture of a giant basilar aneurysm after saphenous vein interposition graft to the posterior cerebral artery: case report. J Neurosurg. 1984;61:387–390. - PubMed
-
- Sekhar L N, Wright D C, Olding M. In: Sekhar LN, Olivera ED, editor. Cranial Microsurgery. New York, NY: 1999. Brain revascularization by saphenous vein and radial artery bypass graft. pp. 581–600. Thieme.
-
- Sundt T M, Piepgras D G, Houser O W, Campbell J K. Interposition saphenous vein grafts for advanced occlusive disease and large aneurysms in the posterior circulation. J Neurosurg. 1982;56:205–215. - PubMed
-
- Sundt T M, Piepgras D G, Marsh W R. In: Sundt TM, editor. Occlusive Cerebrovascular Disease, Diagnosis and Surgical Management. Philadelphia, PA: 1987. Bypass vein grafts for giant aneurysms and severe intracranial occlusive disease in the anterior and posterior circulation. pp. 439–464. WB Saunders.

