Ileocecal intussusception in an adult: the laparoscopic approach
- PMID: 16882431
- PMCID: PMC3016128
Ileocecal intussusception in an adult: the laparoscopic approach
Abstract
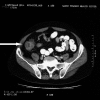
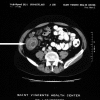
Adult intussusception is uncommon and requires a surgical approach. Malignancy is associated with 31% (43/137) of small bowel intussusception and 70% (74/106) of large bowel intussusception. Computerized tomography (CT) findings are pathognomonic for this condition. Often, the patient presents with long-standing, nonspecific complaints. A 63-year-old man presented with sudden onset of abdominal pain. CT demonstrated colonic inflammation. A laparoscopic right hemicolectomy for ileocecal intussusception was performed. The pathology report revealed a lipoma of the cecum. The postoperative course was uneventful, and he was discharged the fifth postoperative day. Despite a high incidence of malignancy, colonic or ileocecal intussusception can be successfully treated by laparoscopic resection. Review of the literature and treatment options are discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Donhauser JL, Kelly EC. Intussusception in the adult. Am J Surg. 1950; 79: 673– 677 - PubMed
-
- Begos DG, Sandor A, Modin IM. The diagnosis and management of adult intussusception. Am J Surg. 1997; 173: 88– 94 - PubMed
-
- Tan KY, Tan SM, Tan AG, Chen CY, Chng HC, Hoe MN. Adult intussusception: experience in Singapore. Aust N Z J Surg. 2003; 73: 1044– 1047 - PubMed
-
- Toso C, Erne M, Lenzlinger PM, et al. Intussusception as a cause of bowel obstruction in adults. Swiss Med Weekly. 2005; 135: 87– 90 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical