Nonlinear [Ca2+] signaling in dendrites and spines caused by activity-dependent depression of Ca2+ extrusion
- PMID: 16885232
- PMCID: PMC6673787
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1962-06.2006
Nonlinear [Ca2+] signaling in dendrites and spines caused by activity-dependent depression of Ca2+ extrusion
Abstract
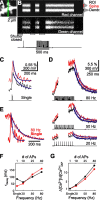
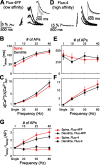
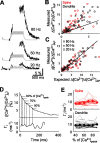
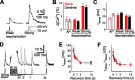
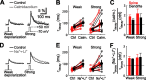
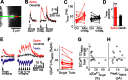
Spine Ca2+ triggers the induction of synaptic plasticity and other adaptive neuronal responses. The amplitude and time course of Ca2+ signals specify the activation of the signaling pathways that trigger different forms of plasticity such as long-term potentiation and depression. The shapes of Ca2+ signals are determined by the dynamics of Ca2+ sources, Ca2+ buffers, and Ca2+ extrusion mechanisms. Here we show in rat CA1 pyramidal neurons that plasma membrane Ca2+ pumps (PMCAs) and Na+/Ca2+ exchangers are the major Ca2+ extrusion pathways in spines and small dendrites. Surprisingly, we found that Ca2+ extrusion via PMCA and Na+/Ca2+ exchangers slows in an activity-dependent manner, mediated by intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ accumulations. This activity-dependent depression of Ca2+ extrusion is, in part, attributable to Ca2+-dependent inactivation of PMCAs. Ca2+ extrusion recovers from depression with a time constant of 0.5 s. Depression of Ca2+ extrusion provides a positive feedback loop, converting small differences in stimuli into large differences in Ca2+ concentration. Depression of Ca2+ extrusion produces Ca2+ concentration dynamics that depend on the history of neuronal activity and therefore likely modulates the induction of synaptic plasticity.
Figures

References
-
- Blaustein MP, Lederer WJ (1999). Sodium/calcium exchange: its physiological implications. Physiol Rev 79:763–854. - PubMed
-
- Bloodgood BL, Sabatini BL (2005). Neuronal activity regulates diffusion across the neck of dendritic spines. Science 310:866–869. - PubMed
-
- Budde T, Meuth S, Pape HC (2002). Calcium-dependent inactivation of neuronal calcium channels. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:873–883. - PubMed
-
- Callaway JC, Ross WN (1995). Frequency-dependent propagation of sodium action potentials in dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 74:1395–1403. - PubMed
-
- Canitano A, Papa M, Boscia F, Castaldo P, Sellitti S, Taglialatela M, Annunziato L (2002). Brain distribution of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger-encoding genes NCX1, NCX2, and NCX3 and their related proteins in the central nervous system. Ann NY Acad Sci 976:394–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
