p38gamma mitogen-activated protein kinase integrates signaling crosstalk between Ras and estrogen receptor to increase breast cancer invasion
- PMID: 16885352
- PMCID: PMC2174269
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4639
p38gamma mitogen-activated protein kinase integrates signaling crosstalk between Ras and estrogen receptor to increase breast cancer invasion
Abstract
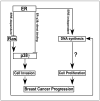
Ras is believed to stimulate invasion and growth by different effector pathways, and yet, the existence of such effectors under physiologic conditions has not been shown. Estrogen receptor (ER), on the other hand, is both anti-invasive and proliferative in human breast cancer, with mechanisms for these paradoxical actions remaining largely unknown. Our previous work showed an essential role of p38gamma mitogen-activated protein kinase in Ras transformation in rat intestinal epithelial cells, and here, we show that p38gamma integrates invasive antagonism between Ras and ER to increase human breast cancer invasion without affecting their proliferative activity. Ras positively regulates p38gamma expression, and p38gamma in turn mediates Ras nonmitogenic signaling to increase invasion. Expression of the Ras/p38gamma axis, however, is trans-suppressed by ER that inhibits invasion and stimulates growth also by distinct mechanisms. Analysis of ER and its cytoplasmic localized mutant reveals that ER additionally binds to p38gamma protein, leading to its specific down-regulation in the nuclear compartment. A p38gamma-antagonistic activity of ER was further shown in a panel of breast cancer cell lines and was shown independent of estrogens by both ER depletion and ER expression. These results revealed that both Ras and ER use distinct pathways to regulate breast cancer growth and invasion, and that p38gamma specifically integrates their antagonistic activity to stimulate cell invasion. Selective targeting of p38gamma-dependent invasion pathways may be a novel strategy to control breast cancer progression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
p38γ mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) confers breast cancer hormone sensitivity by switching estrogen receptor (ER) signaling from classical to nonclassical pathway via stimulating ER phosphorylation and c-Jun transcription.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 27;287(18):14681-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.349357. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22399296 Free PMC article.
-
PTPH1 dephosphorylates and cooperates with p38gamma MAPK to increase ras oncogenesis through PDZ-mediated interaction.Cancer Res. 2010 Apr 1;70(7):2901-10. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3229. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20332238 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of p38γ mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells using metabolomic approach.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019 Feb;107:6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.11.002. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30447427
-
p38γ MAPK Inflammatory and Metabolic Signaling in Physiology and Disease.Cells. 2023 Jun 21;12(13):1674. doi: 10.3390/cells12131674. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between estrogen receptor and growth factor receptor pathways as a cause for endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Jan 15;11(2 Pt 2):865s-70s. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15701879 Review.
Cited by
-
p38gamma MAPK cooperates with c-Jun in trans-activating matrix metalloproteinase 9.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 14;285(20):15149-15158. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.105429. Epub 2010 Mar 15. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20231272 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation and stabilization of topoisomerase IIα protein by p38γ mitogen-activated protein kinase sensitize breast cancer cells to its poisons.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 14;286(41):35883-35890. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.229260. Epub 2011 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21878638 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell Migration Chip for Chemotaxis-based Microfluidic Selection of Heterogeneous Cell Populations.Sci Rep. 2015 May 18;5:9980. doi: 10.1038/srep09980. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25984707 Free PMC article.
-
CDK11p58 inhibits ERα-positive breast cancer invasion by targeting integrin β3 via the repression of ERα signaling.BMC Cancer. 2014 Aug 8;14:577. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-577. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25106495 Free PMC article.
-
p38γ mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) confers breast cancer hormone sensitivity by switching estrogen receptor (ER) signaling from classical to nonclassical pathway via stimulating ER phosphorylation and c-Jun transcription.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 27;287(18):14681-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.349357. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22399296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weiberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Campbell PM, Der CJ. Oncogenic Ras and its role in tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2004;14:105–14. - PubMed
-
- Oft M, Akhurst RJ, Balmain A. Metastasis is driven by sequential elevation of H-ras and Smad2 levels. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:487–94. - PubMed
-
- Huntington JT, Shields JM, Der CJ, et al. Over-expression of collagenase 1 (MMP-1) is mediated by the ERK pathway in invasive melanoma cells. Role of b-raf mutation and fibroblast growth factor signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:33168–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

